Technological advancements have been fundamentally driven by the rising demand for effective, capable, and reliable data storage solutions. Data plays a supreme role in every application that supports the business process. Therefore, it becomes important to enhance the persistence in data storage. Developers should often consider data persistence in their application performance to ensure a seamless experience for users.
Data persistence refers to the permanency of data even after the created application has been closed. Data needs to be saved in a sustainable manner to automate business processes. That’s where the pioneering technology MicroStream comes into play!
MicroStream framework has been gaining traction in recent years because of its acute performance and in-memory persistence capabilities which deliver ultra-fast applications. Read further to explore how MicroStream is reforming the prospect of data persistence.
What is MicroStream and why it is needed?
When the data structure within the memory does not match the data structure in the database, developers need to execute complex and time-consuming query methods to retrieve data. Although the Object Relational Mapping (ORM) frameworks avoid writing database queries, however, these generic frameworks are not reliable and fast to retrieve data.
MicroStream does not require a mapper to store data in memory. This helps developers to directly work with objects, maximizing throughput, and efficiency, minimizing latency, and saving nearly 90% of the power utilized in the mapping process.
The ultimate vision of MicroStream is to modify the database development in the Java Environment. Although Java is commonly known by the term WORA (Write Once Run Anywhere), data persistence in Java applications is complex and expensive. MicroStream is an appropriate solution to store and retrieve complex Java objects.
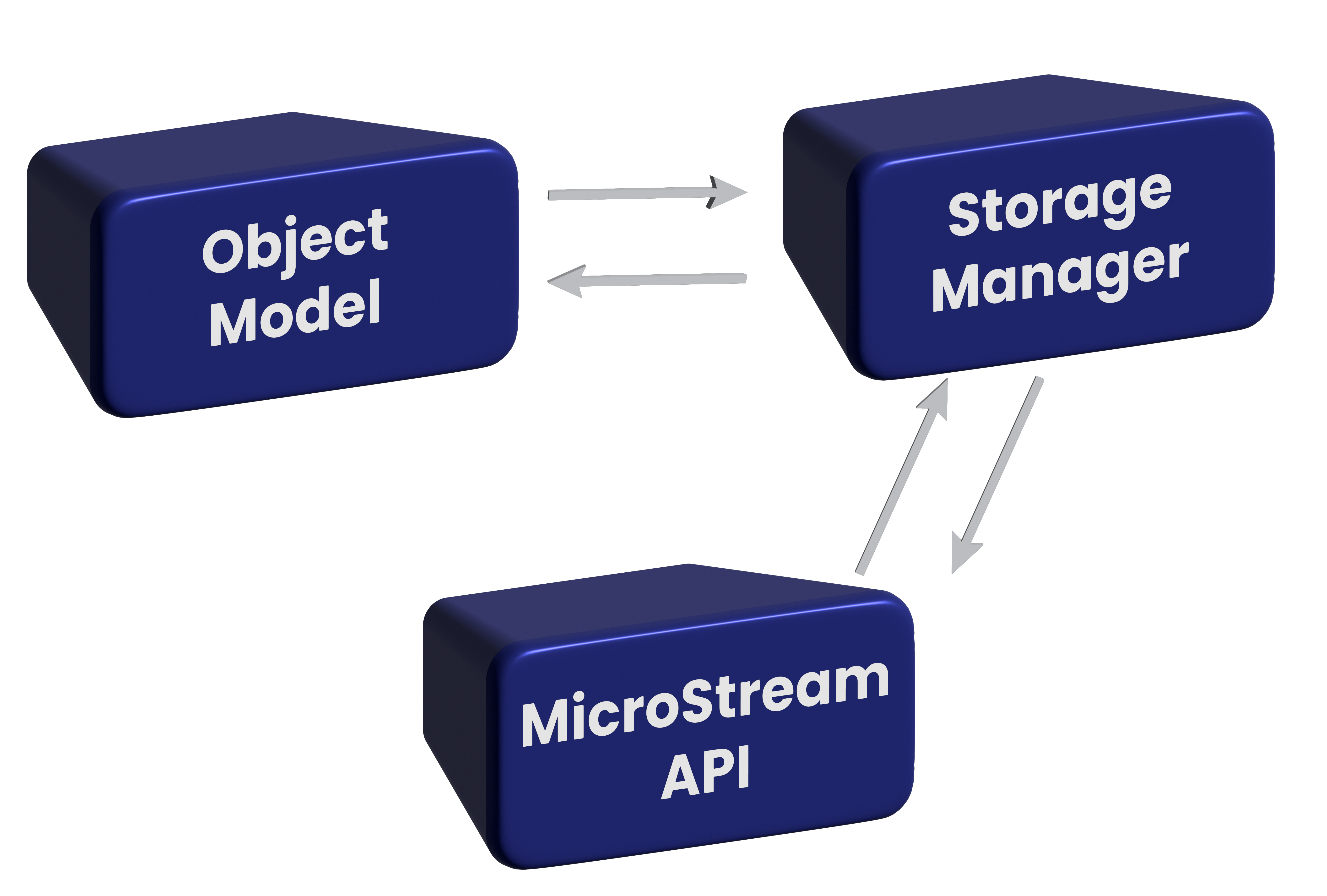
MicroStream is an open-source object graph persistence engine for Java Virtual Machine (JVM) using a custom serialization model and by no means a Database Management System (DBMS). MicroStream supports the storage of any Java object and restores them in memory (Random Access Memory /RAM) in binary format. This persistence layer can be used in distinct environments such as cloud-native microservices, serverless systems, IoT applications, and traditional monolithic applications. Fig.1 shows the basic architecture for MicroStream.
In the MicroStream framework, the data transactions are stored in a highly enhanced serialization byte format (also known as Native-Binary format). Serialization in Java refers to the conversion of an object to a byte stream which can be transmitted over the network. Object Graph meant as the primary data are kept by the Storage Manager. The object model consisting of the data can be quickly accessed using MicroStream APIs. The following table shows the architectural difference between Native persistence and MicroStream.
Table I. Key Differentiators for Native persistence and MicroStream
| Differentiators | Native Persistence | MicroStream |
| Storage Location | Disk | Memory |
| Data Format | Relational | Native-Binary |
| Persistence Procedure | Delta | System Prevalence |
| Intricacies | Medium | Low |
| Performance | Good | Excellent |
| Maintenance | Medium | Low |
In short, MicroStream outstands the conventional persistence methods with its key features such as:
- Ultra-fast in-memory storage – does not demand any ORM or database translation.
- High scalability – to store and retrieve large object graphs in a distributed environment.
- Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness – enables seamless storage of Java objects (any size and complexity) into cloud or binary data stores in compact binary format.
In Brief
MicroStream is a Java-based persistent data storage solution. This cutting-edge technology can realize high-performance and ultra-fast applications with Java. The innovative and superior method of serialization in MicroStream helps developers launch applications that provide a seamless user experience. The added capabilities of MicroStream such as better speed, reliability, simplicity, scalability, and efficiency make it a standard solution for advanced application development. Utilizing the capabilities of MicroStream technology and incorporating it with different databases is a potential methodology that can benefit enterprises in numerous industries.
As a technology-first company and a pioneer in product engineering services, Calsoft specializes in storage engineering and optimization solutions. Calsoft solutions can play a substantial role in supporting this trend.
References
[1] Adrian Bridgwater, “MicroStream persistence framework open sourced”, TechTarget
[2] Why MicroStream, Microstream
[3] Matthew Tyson, “Intro to MicroStream: Super-fast serialization in Java”, InfoWorld






