“Organizations are actively investing in cloud technology due to its potential to foster innovation, create market disruptions, and enhance customer retention to gain a competitive edge,” says Milind Govekar, Distinguished VP Analyst at Gartner.
As a result, IT spending on public cloud services is growing unprecedentedly. By 2024, Gartner forecasts the global spending to hit $679 billion; by 2027, it may soar beyond $1 trillion. Organizations increasingly look to the cloud for infrastructure needs as businesses gain operational freedom and lower infrastructure costs.
Since cloud adoption is widespread today, choosing a suitable model matters even more. Each option presents unique advantages and challenges, making it essential to understand the differences to select the best fit for the business requirements. This blog discusses a combination of public and private cloud solutions and their main differences.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing delivers services like storage, networking, and software through the Internet. You no longer need to rely on physical hardware. Instead, you access these services from providers and only pay for what you use. Here are the standard cloud solutions:
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
Choosing a suitable cloud model impacts your business’s security, cost, and operations. You can choose the public cloud, which saves you money but offers less control. On the other hand, you can get higher security with private clouds but at a higher cost. Hybrid models give you the ability to manage both cost and security.
Now that we’ve covered cloud models, let’s explore why businesses widely adopt public clouds. Also read our latest blog on Cloud Infrastructure Services
What is a Public Cloud?
A public cloud delivers cloud services over the Internet, which multiple companies can access. The provider handles maintenance, security, and updates so you can access the resources without hardware. The key feature of public cloud includes:
- Scalability: You can quickly scale resources up or down based on your needs.
- Cost-Effectiveness: You only pay for what you use. This model helps reduce upfront costs.
- Elasticity and Flexibility: You can adjust resources on demand with public clouds. If your business experiences sudden growth, you can scale up instantly. When the demand decreases, you can scale down just as quickly.
Pros and Cons of Public Cloud
Here’s a clear comparison between the advantages and drawbacks of using a public cloud:
| Pros | Cons |
| Quickly scale resources up or down to match demand. | Less control over infrastructure and how resources are managed. |
| Lower upfront costs due to the pay-per-use model. | Shared infrastructure can pose security risks for sensitive data. |
| Quick setup since the provider maintains infrastructure. | Public clouds may not meet strict regulatory requirements specific to industries. |
| Pay only for what you use, reducing wasteful expenditure. | Switching between providers can be difficult once integrated with a specific public cloud. |
What is a Private Cloud?
A private cloud is an exclusive cloud platform for a company or organization. Unlike public clouds, private clouds are not shared by other users. You can create your own hardware on-premises private cloud or utilize an externally hosted private cloud. The main features are:
- Security and Control: A private cloud provides the most significant level of security. You can use custom protocols to encrypt private information or your solution.
- Configuration: You can allocate customized resources to whatever tools you host in a private cloud. From hardware specifics to software configurations, you can customize everything.
Pros and Cons of Private Cloud
| Pros | Cons |
| You have complete control over data and infrastructure. | Private clouds often come with higher upfront and ongoing costs. |
| You can tailor the infrastructure to meet your exact business needs. | Managing a private cloud requires more technical expertise and resources. |
| Custom security protocols provide more robust protection for sensitive data. | Scaling a private cloud can be slower and more expensive than public clouds. |
Now that you understand private clouds better, let’s explore hybrid cloud models, which blend both public and private cloud environments for maximum flexibility.
Hybrid Cloud: A Combination of Public and Private Clouds
A hybrid cloud is a combination of public and private clouds. It allows you to maintain sensitive data in a secure private cloud while taking advantage of public clouds’ scalability. The key features include:
- Flexibility: A hybrid cloud integrates public and private cloud components. With this flexibility, you can optimize your resources to be at peak performance.
- Scalability with Security: A hybrid cloud balances scalability and security. It lets you scale up your non-sensitive workloads in the public cloud while keeping sensitive information private.
Pros and Cons of Hybrid Cloud
| Pros | Cons |
| Easily switch between public and private cloud based on the workload. | Managing multiple environments can take more work. |
| Use private clouds for sensitive data and public clouds for non-sensitive tasks to save costs. | Making sure both clouds work together can be challenging. |
| You can quickly scale up resources when needed. | Moving data between clouds could expose it to potential risks. |
Businesses can optimize costs with a hybrid cloud by performing less critical operations in a public cloud and more protected data in a private cloud.
With this knowledge, let’s investigate key differences between public, private, and hybrid cloud solutions.
Key Differences Between Public, Private, and Hybrid Clouds
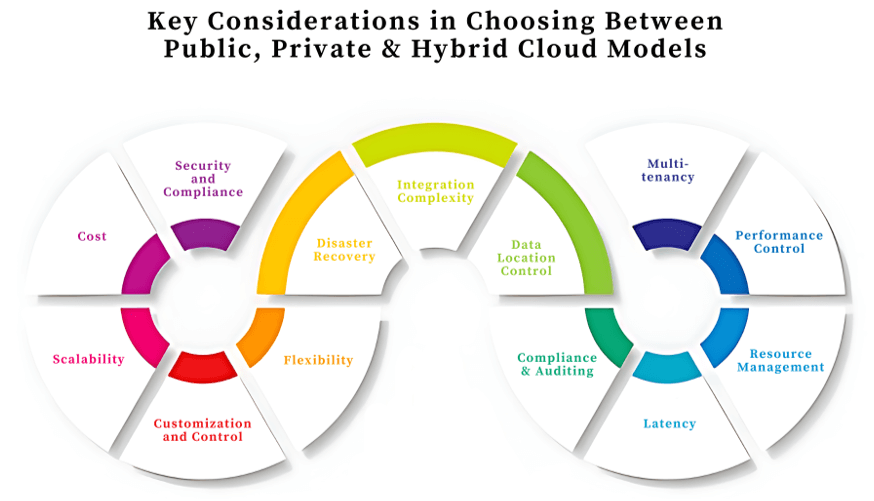
In general, this choice between a public, a private, or a combination of public and private cloud will affect the whole course of your business. Of course, each model comes with a box of pros and cons. Let’s break down the significant differences.
| Feature | Public Cloud | Private Cloud | Hybrid Cloud |
| Security and Compliance | Shared infrastructure, limited control | Full control with custom security measures | Balances public and private security |
| Cost | Pay-per-use, low upfront costs | High upfront costs, ongoing maintenance | Balances costs between public and private |
| Scalability | Rapid scalability adjusts to the demand | Limited by infrastructure capacity | Flexible, scales as needed across clouds |
| Customization and Control | Limited customization | Complete control, full customization | Tailored control over sensitive data |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, wide range of services | Less flexible, designed for specific needs | Combines flexibility of public cloud with private cloud |
| Disaster Recovery | May rely on third-party tools | Strong, in-house capabilities | Uses both public and private for redundancy |
| Integration Complexity | Minimal, managed by provider | Moderate, requires a dedicated team | High, requires seamless integration of both clouds |
| Data Location Control | Data stored in multiple global locations, with limited control | Full control over where data is stored and managed | Allows critical data to be stored in the private cloud while using public cloud for other operations |
| Compliance and Auditing | Limited customization for compliance standards | Full customization for strict industry regulations | Public cloud can be used for non-compliant data, private for compliance needs |
| Latency | Dependent on the internet, subject to varying latencies | Lower latency, more control over network configurations | Critical applications can run in private cloud for lower latency |
| Resource Management | Managed entirely by the cloud provider | Managed internally or by a third-party software | Combines management from both public and private environments |
| Performance Control | Standard performance, shared resources | Dedicated resources provide better performance | Critical applications get high performance in private, non-critical in public |
| Multi-tenancy | Shared resources between multiple customers | Single tenant environment with full resource access | Combines multi-tenancy benefits with dedicated resources for key operations |
With critical technical distinctions clear, the next step is understanding some use cases of various cloud solutions.
Use Cases for Public, Private, and Hybrid Cloud
When considering cloud solutions, different businesses and sectors benefit from a combination of public and private cloud. Now, let’s break down some specific use cases for public, private, and hybrid clouds tailored to different industries and business needs.
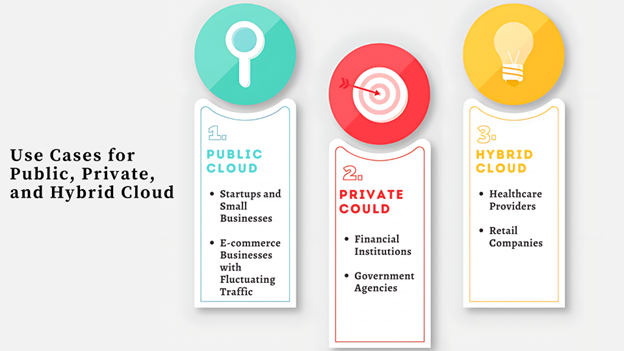
Public Cloud
- Startups and Small Businesses: Public clouds are excellent options for startups and small businesses. They allow you to scale without the heavy costs of infrastructure. You can use services like AWS or Google Cloud to access computing power and storage without a significant investment.
- E-commerce Businesses with Fluctuating Traffic: Public clouds are perfect if your business deals with varying traffic, like an e-commerce platform. You can scale up your resources during peak times to handle the extra traffic. You can scale back once the demand slows down, avoiding unnecessary expenses.
Private Could
- Financial Institutions: Controlling and securing sensitive data is critical in the financial sector. You can store and manage sensitive customer data securely and in a controlled environment.
- Government Agencies: Government organizations often handle classified information. You can implement strict security measures that comply with national security regulations.
Hybrid Cloud
- Healthcare Providers: Secure patient data management is crucial in healthcare. You can keep your data in a private cloud while using public clouds for less critical stuff, such as telemedicine.
- Retail Companies: You should run a private cloud when handling payment data. The rest of your IT workload can be migrated to public clouds.
Now that you know where different cloud models work best, let’s look into the key factors you must evaluate to choose the right one for your organization.
How to Choose the Right Cloud Model for Your Business
To find the right cloud model, start by evaluating your business’s unique needs. First, analyze your data sensitivity to determine the level of security and control you require. If you handle sensitive data, choose a private or hybrid cloud. Choose public cloud if your data doesn’t need strict security.
Next, consider your compliance obligations. Many industries have strict regulations regarding data management and storage. If you need to meet these regulations, think about a private cloud or a hybrid solution.
Don’t forget to weigh cost flexibility. Public clouds usually offer pay-per-use models, which can save you money if your business experiences unpredictable growth. However, private clouds might have higher costs but can provide consistent long-term expenses that are ideal for companies with stable workloads.
Is it possible to switch cloud models?
Yes, businesses can transition between cloud models as their requirements evolve. Many organizations initially adopt public clouds due to lower costs and easier setup, then migrate to private or hybrid models as they scale or require enhanced security and control.
Hybrid clouds provide flexibility, cost-efficiency, and scalability. This model allows businesses to securely manage sensitive data in a private cloud while utilizing the public cloud’s cost-effectiveness and computational power for less critical tasks. It also supports a steady approach to cloud adoption, enabling businesses to adapt as their fluctuating needs over time.
Wrapping Up
As businesses scale, cloud computing needs become increasingly important, and a well-chosen cloud solution can significantly enhance competitiveness. Public clouds offer scalability and cost savings, making them ideal for startups, while private clouds provide complete control and flexibility, crucial for those handling sensitive data. In contrast, hybrid clouds combine these benefits, enabling organizations to scale effectively while maintaining appropriate security measures.
Before committing to a cloud solution, it’s essential to carefully assess business requirements and develop a cloud strategy tailored to the specific use case. Relying on a one-size-fits-all approach can be limiting, and exploring how a hybrid cloud model offers both flexibility and scalability is crucial.
Calsoft leverages its 25 years of product engineering expertise and extensive domain experience to transform business operations through innovative cloud solutions. Calsoft provides end-to-end cloud solutions, from strategy and planning to deployment, monitoring, and management of your platform, so that you can drive business alignment.