Cloud computing has emerged as a dominant force in today’s technological landscape. In the current digital era, cloud computing offers businesses the flexibility to digitize necessary aspects of their operations without the significant investment in on-premises hardware. Consequently, workforce can access the necessary applications and tools from any location around the world, enhancing productivity and operational agility.
Rather than installing and maintaining applications, storage solutions, and powerful compute processors on-site, organisations can rely on cloud providers to deliver these resources. This setup enables access to computing capabilities from anywhere with an internet connection. Cloud infrastructure allows businesses to utilize servers in remote data centers instead of relying on local desktops or laptops.
Cloud Infrastructure Services provide the essential foundation for modern computing by offering businesses access to virtualized resources such as servers, storage, and networking, all hosted in remote data centers. This facilitates organisations to scale their IT capabilities without the need for significant investments in physical hardware. By leveraging cloud infrastructure, businesses can deploy, manage, and scale applications with greater flexibility and efficiency. These services support a wide range of use cases, from hosting websites and applications to data analytics and Artificial Intelligence (AI), enabling organizations to stay scalable, flexible, agile and competitive in an evolving digital world.
According to Statista reports, 73% of enterprises have shifted to hybrid cloud solutions, moving beyond traditional single-cloud setups. The need for more flexibility, security, and cost management steers this change.
Cloud infrastructure services offer the flexibility of a public cloud while maintaining the control of a private cloud. With it, you can customize infrastructures to fit your exact needs.
This blog explores how cloud infrastructure services can enhance your business covering the latest trends, key strategies and practical steps to improve your cloud strategy.
What are Cloud Infrastructure Services?
Imagine you have a company, but instead of building a big, fancy office, you just rent a space whenever needed. That’s how cloud infrastructure works. It allows businesses to use servers, storage, and networking over the internet. You can think of it as a virtual toolbox that’s always available.
At its core, cloud infrastructure includes servers, storage, and networking. You use these key pieces to access computing power, store data, and connect various systems. Let’s break down these components so you can clearly understand how each one works.
- Servers: Servers act as the engines driving all the processing power in the cloud. They run your applications and handle all computations.
- Storage: Storage is where all your data resides, from simple documents to complex databases. In the cloud, your storage scales according to your needs.
- Networking: Networking connects everything in your cloud environment. You can ensure your data flows smoothly between servers, storage units, and users.
Cloud Infrastructure vs. Cloud Computing vs. Cloud Architecture
To help you understand the differences, let’s compare cloud infrastructure, cloud computing, and cloud architecture side by side:
| Aspect | Cloud Infrastructure | Cloud Computing | Cloud Architecture |
| What It Is | The physical and virtual resources like servers, storage, and networking. | The delivery of computing services (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) over the internet. | The design and structure of a cloud environment, including all the layers. |
| Key Components | Servers, storage, networking, and virtualization tools. | Online platforms offer services such as databases, storage, and computing power. | The strategic layout of how cloud resources and services interact and are managed. |
| Role | Provides the necessary resources to run your cloud services. | It uses infrastructure to deliver services to you over the Internet. | Directs how you deploy and organize cloud services to meet specific needs. |
| Examples | Data centers, virtual machines, and storage are available from providers like AWS. | Applications like Google Drive (SaaS) and computing services like AWS EC2 (IaaS). | Microservices or serverless architectures that you use to optimize resource efficiency. |
In short, cloud infrastructure provides resources, and cloud computing delivers services through those resources. On the other hand, cloud architecture organizes everything so that they work efficiently together.
Now that you understand the basics of cloud infrastructure services, it’s time to examine how these components interact in different cloud computing models.
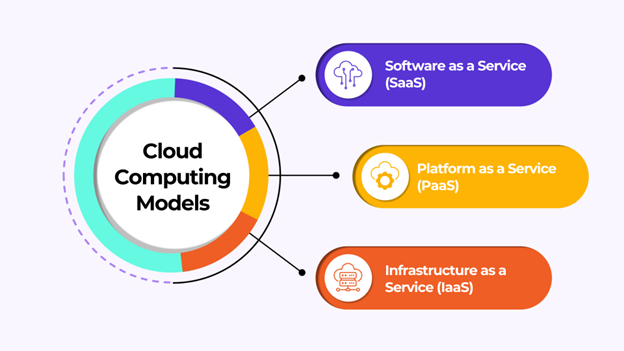
Types of Cloud Computing Models
Cloud computing frameworks include accessing and managing cloud resources. Each framework, SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS, provides varying levels of control, flexibility, and administration to meet various business objectives. Let’s look at each one in depth.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
You can access software programs directly via the Internet using the SaaS framework. The service provider handles everything, including hosting, maintenance, and updates. As a result, you may focus on the application’s core functionality while avoiding infrastructure issues.
Benefits:
- You can work from anywhere and on any device if you have an internet connection.
- You do not need to install or upgrade your computer or device software.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS lets you use a cloud platform to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure typically associated with developing and launching an app.
Benefits:
- PaaS providers manage infrastructure, letting you focus on development responsibilities.
- PaaS platforms in the cloud enable you to construct and grow apps.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
With an IaaS, you can have complete control over virtual computing resources. IaaS allows you to rent IT resources like servers and storage on a pay-as-you-go basis. Hence, it is perfect for situations requiring a customized IT environment.
Benefits:
- Customize virtual resources to match your individual needs.
- IaaS enables you to scale your IT resources up and down as your business requirements change.
Now that you understand the distinctions among these cloud computing frameworks within cloud infrastructure services let’s explore public, private, and hybrid cloud architectures.
Comparing Public, Private, and Hybrid Cloud Architectures
When you assess cloud infrastructure services, you’ll identify three primary cloud architectures: Public Cloud, Private Cloud, and Hybrid Cloud. Additionally, some organizations use Community Cloud, which is shared by several organizations supporting specific communities. Each architecture has distinct advantages and caters to different requirements, whether you prioritize security, scalability, or cost efficiency.
- Private Cloud: This setup is exclusively for one organization. You get complete control and higher security. This makes it ideal if you handle sensitive data or need to meet strict regulations.
- Public Cloud: In this model, you use shared resources from third-party vendors. It’s cost-effective and easily accessible, which is excellent if you need flexibility without heavy infrastructure investments.
- Hybrid Cloud: This architecture combines private and public clouds. It balances a private cloud’s security with a public cloud’s scalability. It works well if your workloads vary, or you need a mix of secure and scalable environments.
| Aspect | Private Cloud | Public Cloud | Hybrid Cloud |
| Key Benefits | You get high control, tailored security, and meet compliance needs. | You benefit from lower costs, scalability on demand, and less management. | You gain flexibility, better performance, and a balance between control and scalability. |
| Typical Use Cases | It is ideal for industries with strict regulations like finance and healthcare. | Works well for startups, small businesses, and workloads that change often. | Perfect if you need both security and the ability to scale with the public cloud. |
| Cost | Higher upfront and ongoing expenses due to dedicated infrastructure. | Lower costs due to shared resources and pay-as-you-go models. | Costs vary based on your mix of public and private resources. |
| Scalability | Limited to the infrastructure you control. | Highly scalable, with resources available when you need them. | You can scale resources up or down by shifting between private and public clouds. |
| Security | You control security with dedicated resources and custom protocols. | Standardized security, but less customizable than private clouds. | Security is tailored based on which cloud handles specific tasks. |
Now that you understand these cloud architectures let’s look at the benefits of cloud infrastructure services. Also read Virtualization in Cloud Computing
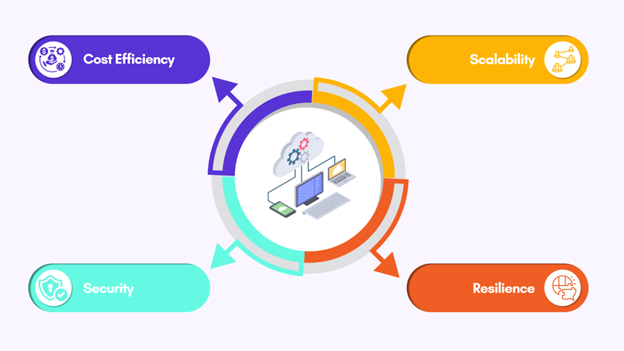
Benefits of Cloud Infrastructure Services
Cloud infrastructure services provide essential benefits that significantly enhance your business’s operations and management. You can adjust resources quickly, scale operations efficiently, and save on costs. This approach strengthens your data security, ensuring you stay agile in meeting changing demands while reducing expenses and improving your IT capabilities.
Cost Efficiency
Using cloud infrastructure services cuts down on expenses. You only pay for the necessary resources instead of pouring money into physical hardware. This approach helps you avoid hefty upfront costs and manage your budget more precisely. You align your spending with your needs, making your financial planning more accurate.
Scalability
As your needs change, you may adapt your resources immediately. If demand increases, you scale up. If it slows down, you scale back. This guarantees that your infrastructure matches real-time demands, reducing waste and downtime.
Security
Security measures ensure the security of your data through encryption, multi-factor authentication, and constant monitoring. These built-in security safeguards eliminate the need to manage every security aspect independently. You keep control while ensuring your data is safe and meets industry standards.
Resilience
You employ reliable disaster recovery and backup solutions to keep your data secure and your operations functioning during calamities. Frequent backups and redundancy allow you to swiftly recover from disturbances, reducing downtime and safeguarding your brand.
Now that you’ve seen these benefits let’s discuss the critical considerations for adopting Cloud Infrastructure.
Critical Considerations for Adopting Cloud Infrastructure
Cloud infrastructure involves setting up the technology and ensuring that every other aspect of your operation fits in with the cloud environment. Let’s examine some pointers to help you adopt the proper cloud infrastructure.
- Operational Governance: Extend your existing governance frameworks to cover cloud operations. It will ensure control and consistency across all your business processes.
- Scalability Planning: Consider how you will change the resources in your cloud when your needs change. You should have a clear plan to scale up or down without overcommitting to too many resources or failing in delivery.
- Risk of Vendor Lock-In: You should not depend on one cloud service provider. Diversify to stay adaptable and avoid relying heavily on a single vendor’s services.
- Data Residency Compliance: It is the compliance your storage practices should guarantee that the local laws and regulations of where and how your data is stored or processed are duly followed, or a severe threat of legal problems may arise.
- Security Measures: To protect your data, implement robust security practices, like encryption and multi-factor authentication. It’s your responsibility to ensure your data remains secure, even if a provider manages the infrastructure.
- Skills and Expertise: Evaluate whether your team has the right skills to manage cloud infrastructure effectively. If not, consider training or partnering with experts to fill the gaps.
Now, we shall move to the section on future trends in cloud infrastructure. This will keep you abreast of the latest happenings and facilitate intelligent decision-making as these technologies develop.
Future Trends in Cloud Infrastructure
While you forge ahead with cloud infrastructure, several trends shape how you administer and optimize your cloud environment. These strategic shifts impact your level of competitiveness.
Grasping these developments is critical to making informed decisions that give your operations an advantage in the long run.
Edge Computing
Edge computing represents the future of data processing. This technology reduces latency significantly because it processes data closer to its point of origin, which is critical for applications such as autonomous vehicles, smart cities, industrial IoT, healthcare systems, and more. Localized data processing results in faster response times and reduced bandwidth usage, thus enhancing the handling of tasks with time sensitivity.
AI and Machine Learning in Cloud Management
AI and machine learning rapidly transform cloud management. These technologies automate routine tasks, optimize resource use, and predict most problems before they impact operations. Integrate AI into your cloud strategy to increase efficiency, reduce downtime, and manage complex workloads more precisely.
Sustainability and Green Computing
Sustainability is a growing focus in cloud infrastructure. Many leading companies like Google and Microsoft are investing in more energy-efficient data centers, renewable energy sources, and environmentally friendly computing techniques. This trend aims to reduce environmental impact while cutting running costs and making infrastructure more sustainable and profitable.
Conclusion
Choosing cloud infrastructure services goes beyond technology; it represents a strategic investment in any organization’s future.
Cloud infrastructure provides new scalability, cost savings, and operational security potential, resulting in unparalleled growth and innovation. To succeed, focus on encouraging change and creativity, using all the opportunities the cloud provides.
By leveraging cloud infrastructure, organizations can streamline operations, enhance agility, and quickly adapt to changing demands without the need for significant investments in physical hardware. Whether it’s for hosting applications, managing data, or supporting advanced technologies like AI, Cloud Infrastructure Services empower businesses to innovate and grow efficiently, ensuring they remain at the forefront of their industries.
Calsoft leverages its 25 years of product engineering expertise and extensive domain experience to transform business operations through innovative cloud solutions. Enabling businesses adopt cloud-first approach with our established cloud & infrastructure practices.