SDN is a crucial technology in a roadmap for a dynamic and intelligent network, be it enterprise level connecting several devices on-premises or branches across the wide area (SD-WAN). With the power of SDN technology, telecom operators are taking it to achieve central control over the network and compute nodes.
As the 5G going mainstream disruption for telecom as well as technology business players, there is a growing need to handle data flows within the network in real time along with smartly minimizing bandwidth usage plus latency. The emergence of SDN and NFV technologies had majorly set up a foundation to build a network having expected requirements for end users along with a dynamic and central control for service providers or enterprises.
In this article, let us discuss about SDN stack, Tungsten Fabric and how it can be used for 5G-network edge cloud that is based on Akraino Edge Stack.
Tungsten Fabric is an open source SDN initiative from Juniper and merged into Linux Foundation as a community project. TF provides a single point of control, visibility, and management for networking & security for different types of data center deployments or clouds. It has taken SDN technology to next level by
- Providing consistent network functionality and enforcing security policies for different types of workloads (virtual machines, containers, bare metal) orchestrated with different available orchestrators (OpenStack, Kubernetes, VMware , etc)
- Providing production grade networking & security stack for Data Center and Public Clouds (AWS, Azure, GCP) & Edge cloud deployments
Tungsten Fabric evolved as a network software stack for providing an SDN solution for Telco Cloud and NFV use cases.
To understand the application of TF for telco cloud, let us discuss about the PoC proposed by Juniper’s Sukhdev Kapur to Linux Foundation’s Akraino community (an open source software stack for network edges). This proof of concept is approved by the Akraino.
Tungsten Fabric Integration with Akraino based Network Edge Cloud
TF, by integrating with Akraino Edge Stack, can act as unified SDN controller to enhance many features for 5G core and edge nodes, including
- Enabling distributed edge computing using TF remote compute architecture,
- A common SDN controller for different workloads in network cloud i.e. CNF, VNF, PNFs
- Service chaining at different types of edge sites or clouds (public or private)
- Common security policy enforcement for all nodes
- Advanced networking performance features: SR/IOV, DPDK, BGP-VPN, IPSec/TLS Support, etc
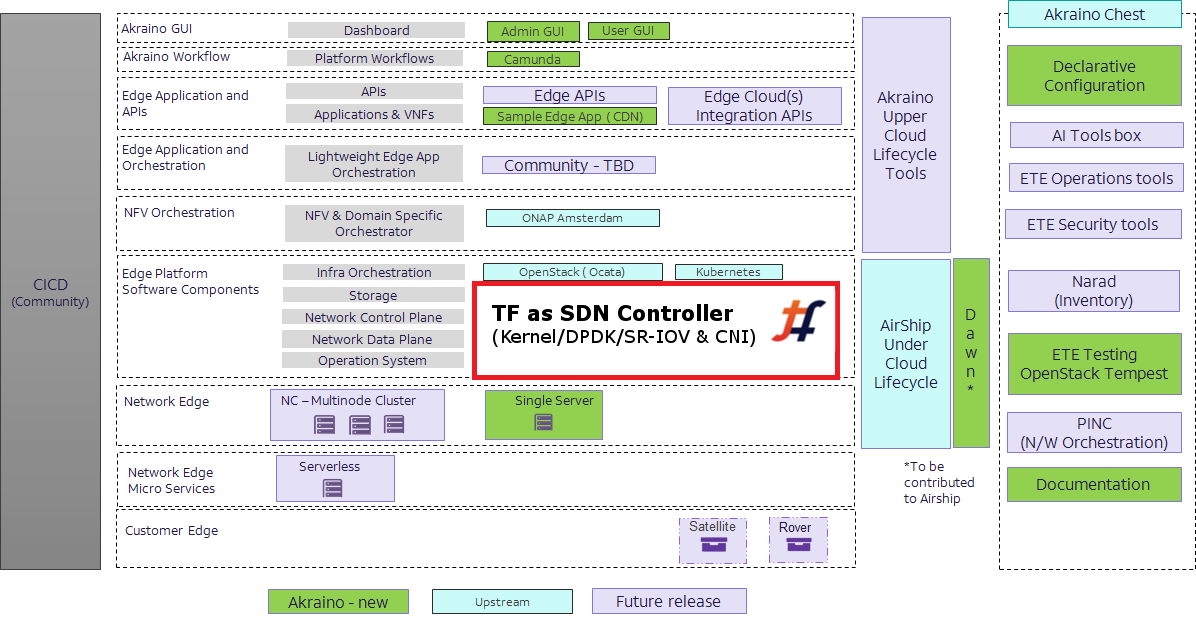
Image source: Akraino Reference architecture
You can see from above image, like other open source projects, TF place at edge platform software component, enhancing with new feature set to act as unified SDN controller for any type of workload & compute orchestration.
Deployment
Tungsten fabric is composed of components like controller and vRouter; plus additional components for analytics and third party integration. In this PoC, TF integrates with Kubernetes (CNI) and OpenStack (Neutron) as SDN plugin to enable rich networking capabilities and lifecycle management of VMs and containers where TF components or control functions deployed.
The configuration declared at the central data center is enforced on edge nodes to set up consistent network and security policies. The deployment and life cycle management of Tungsten Fabric can be done with tools like Ansible or Helm. These configuration files are termed as playbooks if Ansible is used or charts in case of Helm. These tools provides benefits of automation and management of components, further reducing operational costs for edge deployments.
Tungsten fabric along with Helm offers a seamless solution where TF services are deployed in containers using a microservices architecture to enable advantages like self-healing, updates, CI/CD, etc. Helm uses Kubernetes to declare charts for subsequent microservices, allowing greater automation in managing TF services. In this case, Kubernetes become a single orchestrator to manage lifecycle of all control operations. Such integrated solution evolved as Tungsten Fabric Helm (TF Helm).
OpenStacks’s Airship (Armada) is an umbrella project with which TF integrates for installation using helm charts and set up interaction with edge nodes using CNI and Neutron.
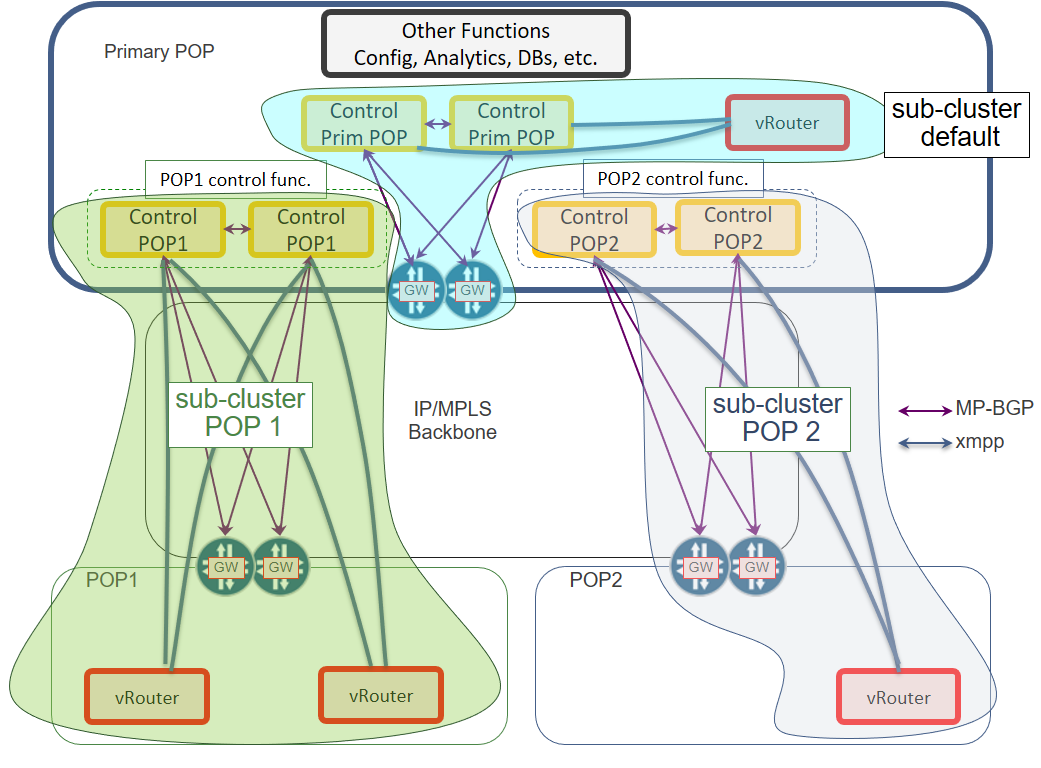
The basic idea behind this PoC is to define an architecture for a distributed Edge Cloud keeping operational and deployment cost low. Another objective is to build a network where failure of any edge node application should not hamper availability and functionality of edge network to avoid traffic loss. To implement such architecture, a solution proposed in this PoC exercise utilizes the same TF based on a single SDN cluster that spans across all the edge nodes. A central SDN cluster located at main data center will have TF installed with Kubernetes and OpenStack orchestrators along with TF control components. Dedicated control functions, which handles compute and networking operations for all edge nodes, are located at the central data center, and connected to vRouter (TF component) set at the edge nodes using set of gateways. The dedicated control function is logically present at the Primary POP to control vRouters of the edge nodes located on the remote POPS. MP-BGP protocol is used between SDN Gateways and control functions, and XMPP is used for communication between vRouters and dedicated control functions.
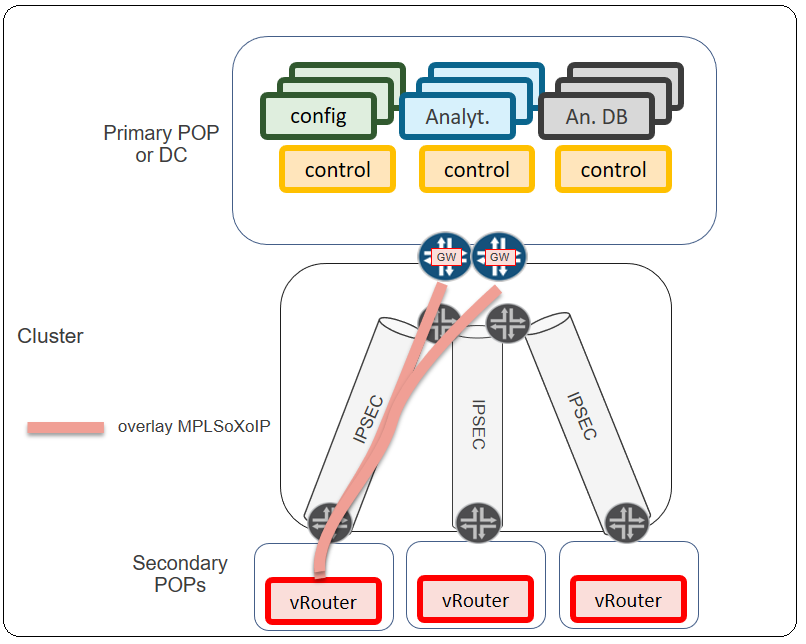
To have an end-to-end data transmission, an overlay network is established between edge nodes and central data centers in which MPLS over IP (MPLSoXoIP) is used. Communication between gateways can optionally use IPsec encryption to protect network data.
Summary
TF has emerged as a leading SDN solution with every release. Deployment of TF using helm charts and orchestration of every type of workloads from a diverse set of clouds has increased the potential of TF for Telco use case. Akraino Edge Stack is pre-integrated with a set of projects, which promotes various orchestrations and performance benefits. Integration of TF with Akraino edge stack enable enhanced features and utilizes remote compute architecture of TF. A solution can orchestrate all types of workloads like PNFs, VNFs and CNF, implement service chaining at edge sites, workload and data transfer security, automating deployment of control functions and workloads, and more.






