How do you minimize the risk of a cyber-attack when connecting public and private clouds?
When you deploy hybrid clouds, the attack surface increases, as integrating your private cloud with a public one creates additional entry points that attackers can target.
As businesses increasingly adopt hybrid cloud models, ensuring security across both public and private infrastructures becomes a significant challenge. According to Gartner, by 2025, 85% of organizations will have a cloud-first principle, which makes securing hybrid environments more critical than ever. Hybrid cloud security introduces complex issues such as managing data protection, ensuring consistent security policies, and addressing compliance across multiple environments.
Moreover, cybercriminals are becoming increasingly sophisticated, and even the smallest security gap may leave the whole infrastructure vulnerable.
This blog closely examines the challenges surrounding hybrid cloud computing, the entailing risks, and some practical strategies to help safeguard it, including the best ways to secure your network.
This will help you clearly understand the unique hybrid cloud challenges, and you will walk away with actionable steps to safeguard your data and systems.
What is Hybrid Cloud Security?
Imagine you’re running two different workspaces, one shared and the other private. Each has its advantages, but you can choose where to do each task when you connect them. That’s what a hybrid cloud does—it merges public and private clouds.
- In a public cloud, you’ll find economies of scale. It’s cost-effective because you share infrastructure with others.
- With a private cloud, your organization has more control, often for sensitive operations. Here, you can keep your data in a more isolated, secure environment.
But it gets tricky here: you need to manage security across these two environments.
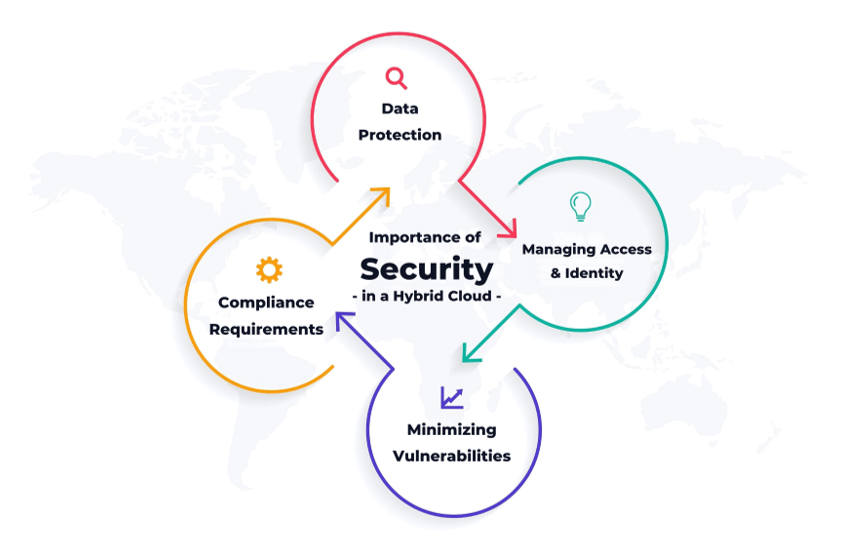
Why is Security Important in a Hybrid Cloud?
Now, let’s talk about why securing the cloud—especially a hybrid one—is essential. When you move to the cloud, your data and services spread across various environments. That means security risks can multiply if you do not manage them correctly.
Here are some hybrid cloud challenges:
- Your data often moves between private and public clouds. Without encryption or proper access controls, it could be intercepted or exposed.
- When you can’t see all your data flows, security blind spots appear, making it harder to track threats.
- Each environment might have its rules, and aligning security practices across both can be a significant challenge.
Now that you comprehend the basics of hybrid cloud challenges and security, let’s examine the various challenges in detail.
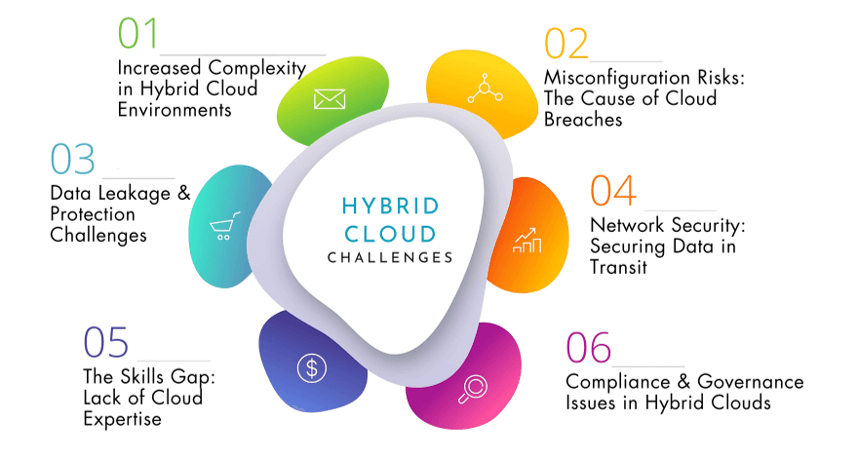
Top 6 Hybrid Cloud Challenges
Managing a hybrid cloud isn’t just about combining environments; it’s about overcoming unforeseen challenges as your infrastructure scales. Let’s start with our first challenge: the complexity of handling multiple cloud environments effectively.
1. Increased Complexity in Hybrid Cloud Environments
Hybrid cloud environments have different systems working together but with distinct security protocols. This creates complexity, and with complexity comes risk.
Furthermore, it also increases the operational intricacy because what works in one environment may not quickly transfer to another. It’s like trying to merge two completely different roadmaps into one—it’s possible, but the navigation will become tricky.
Here are some hybrid cloud challenges you will face:
- Visibility Issues: Security teams often lack real-time visibility into how data is accessed and stored across environments.
- Inconsistent Security Policies: Different cloud providers may have different security standards, making it difficult to enforce consistent policies.
- Threat Detection: Identifying threats across multiple environments is more complex because each cloud has its own logging and alerting mechanisms.
The security team needs to:
- Monitor both public and private cloud environments.
- Manage different security protocols.
- Ensure compliance across various cloud infrastructures.
This overwhelming workload often leads to missed alerts, miscommunication between teams, and an inability to respond to threats quickly.
2. Misconfiguration Risks: The Cause of Cloud Breaches
Misconfiguration of systems is a common cause of hybrid cloud challenges for organizations. A single mistake—like leaving an open port or failing to set the correct permissions—can expose critical data to the world.
Misconfiguration occurs when security settings or infrastructure configurations are incorrectly applied or left incomplete. Because cloud setups are dynamic and flexible, misconfiguration is often a problem in hybrid cloud environments. There are multiple moving parts, and keeping track of them is hard.
For example:
- Exposed databases because permissions were not set correctly.
- APIs are left vulnerable due to a lack of encryption.
- Open ports that should have been closed after deployment.
Why does this happen so often? We have seen that hybrid cloud environments are complex. Its flexibility, while beneficial, also makes it prone to errors. Teams usually work fast, deploying new applications or scaling services, but security settings can easily get overlooked in the rush.
- Each environment has its own management tools, making it easy for security configurations to get out of sync.
- With so many manual steps in configuring cloud environments, mistakes are inevitable.
- Not all security teams have the expertise to manage hybrid cloud configurations properly.
Here’s what misconfigurations look like in real life:
- Open S3 Buckets: A well-known issue with AWS. Many organizations forget to configure these storage spaces, exposing sensitive data properly.
- Unpatched Vulnerabilities: Hybrid clouds often rely on multiple software layers. Failing to patch vulnerabilities can create backdoors for attackers.
- Improper Access Controls: Forgetting to limit who can access specific resources leaves sensitive areas of your cloud infrastructure wide open.
Misconfigurations might be expected, but they’re avoidable with the right tools and practices.
3. Data Leakage and Protection Challenges
Data leakage is one of the top hybrid cloud challenges you’ll need to address. It occurs when sensitive information is exposed or transferred to unauthorized parties.
Imagine you’re passing a highly confidential message between two friends. Someone could intercept the message if it isn’t sealed correctly, or the route isn’t secure. That happens in hybrid clouds if you do not place proper protections. Data often moves across networks between the public and private cloud. This data can become vulnerable to theft or exposure without robust encryption or access controls.
There are several reasons why data leaks occur in hybrid clouds:
- Insecure APIs: APIs connect different parts of your cloud, but attackers can exploit them to access data if they’re not securely configured.
- Poorly Secured Endpoints: Devices or applications connecting to the cloud can serve as entry points for malicious actors.
- Misconfigured Access Controls: Failing to limit who has access to sensitive data is a significant cause of leaks.
You can take measures to decrease the risk of data leakage significantly:
- Encryption: Always encrypt data both in transit and at rest. Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted.
- Secure API Gateways: Use gateways that authenticate and protect your APIs. With it, only trusted systems can interact with your data.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tools: Implement DLP solutions that monitor and block unauthorized attempts to transfer sensitive data from your system.
These steps form a solid defense against the inherent risks of data moving through multiple clouds.
4. Network Security: Securing Data in Transit
When you’re managing a hybrid cloud, securing data in transit is a constant concern. Data doesn’t just sit in one place; it moves between the public and private clouds. The more data you move between these two environments, the higher the risk of someone intercepting it. Therefore, you need to ensure that all communication pathways are secured.
There are several hybrid cloud challenges when securing your data:
- Different Network Configurations: Each cloud provider may have different networking setups, making it difficult to secure the entire infrastructure uniformly.
- Data Traffic Visibility: Tracking data flows across public and private clouds is often problematic. This creates blind spots where your security teams may miss suspicious activity.
- Traditional Network Security Shortcomings: Standard firewalls and security measures might work well for on-premises networks. However, they often don’t translate to a hybrid cloud setup where data moves through multiple external networks.
Here are the best ways to keep your network secure:
- Use VPNs: A Virtual Private Network (VPN) forms a secure tunnel for data to travel between clouds.
- Encrypt Data in Transit: Just like encrypting data at rest, you need to encrypt data while it’s being transferred.
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA): Adopt a Zero-Trust model in which no user or device is trusted by default.
When you apply these strategies, you can create a secure network that ensures data remains protected even as it travels between clouds.
5. Bridging the Cloud Expertise Gap: Expanding Opportunities
Traditional on-premises security often relies on static environments with fixed controls. However, in a hybrid cloud, everything is dynamic. You’re managing security across public and private clouds, each with different systems. The skills that worked for on-prem environments won’t be practical with a hybrid cloud setup.
When your team lacks the right skills, it leads to:
- Misconfigurations: This is the most common result of a skill gap. Your team can expose APIs without proper knowledge or fail to set appropriate access controls.
- Failure to Detect Threats: Real-time threat detection tools are essential in a hybrid cloud. Teams untrained in cloud environments may fail to monitor suitable systems.
Here’s how you can close the gap and ensure your team is ready to secure a hybrid cloud:
- Invest in specialized cloud security training programs that focus on hybrid environments. Look for courses on AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud security certifications.
- If your team isn’t ready, you can work with managed security services (MSS), such as Calsoft Inc. These external experts can help monitor and secure your hybrid environment while your internal team builds expertise.
6. Compliance and Governance Issues in Hybrid Clouds
When you use a hybrid cloud, compliance becomes more complex. You’re dealing with multiple cloud providers, each with its own governance frameworks. To keep everything in check, you need a solid strategy that ensures compliance across all environments.
For example, data stored in a public cloud might reside in a different country, requiring strict adherence to local regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
Multi-cloud governance can be difficult because:
- Each cloud provider handles compliance differently.
- You need to ensure that security policies are consistently applied across all environments.
- Some workloads require more stringent controls than others.
When you use the shared responsibility model, security is a shared responsibility between you and the cloud provider, where:
- Cloud providers are accountable for securing the infrastructure.
- You are responsible for securing the data, applications, and configurations within the cloud.
Many organizations assume the provider handles everything, which is not the case. By setting the proper security controls, you must ensure you’re meeting your end of the deal.
Here’s how you can stay compliant in a hybrid cloud:
- Regularly conduct audits to ensure your hybrid cloud setup adheres to relevant regulations.
- Use tools with which you can manage security policies across multiple environments.
Solutions to Challenges and Risks in Hybrid Cloud Security
To tackle hybrid cloud security challenges effectively, follow these steps:
- Develop a comprehensive policy that covers both public and private clouds.
- Schedule quarterly security audits to identify vulnerabilities and maintain compliance with industry regulations.
- Use cloud security platforms that offer automated threat detection, encryption, and compliance monitoring. This will enhance your visibility and response capabilities.
- Implement a Zero-Trust framework. It requires continuous verification of user identities and enforce strict access controls.
- Provide regular training focused on hybrid cloud security. Equip your team with the skills they need to manage risks effectively.
By implementing these strategies, you can mitigate risks and enhance your hybrid cloud security.
Also read our latest blog on Cloud Security Automation
Using Cloud Security Platforms and Managed Services
Managing hybrid cloud challenges and security can be overwhelming. That’s where cloud security platforms and Managed Security Services (MSS) come into play. These tools provide:
- Centralized management of all your security protocols.
- Automated threat detection to catch issues before they become critical.
- 24/7 monitoring, ensuring that your hybrid cloud is constantly under watch, even when your team isn’t available.
Conclusion
Addressing hybrid cloud security challenges is crucial for businesses to maximize the benefits of their cloud infrastructure. From managing data across multiple environments to ensuring consistent security policies, organizations must adopt a proactive approach to mitigate risks. By leveraging advanced encryption, implementing zero-trust models, and maintaining strict compliance, businesses can strengthen their hybrid cloud defenses. Educating teams and investing in cloud security expertise also plays a key role in closing the skills gap. As the cloud landscape continues to evolve, staying updated with emerging threats and security strategies is essential to ensure a secure, scalable, and resilient hybrid cloud environment.
Calsoft, being a technology-first partner offer businesses seamless integration between public and private cloud environments, ensuring optimal flexibility and scalability. By focusing on security, compliance, and data management, Calsoft helps organizations create robust cloud architectures tailored to their specific needs. Our hybrid cloud capabilities help optimize the cloud within the business framework.