Industries had undergone three revolutions till. First being, mechanization and using indirect combustion for powering up mechanization through water and steam power (Industry 1.0). Second revolution brought complicated machinery for mass production and used electrical power (Industry 2.0). Automation, Computers and internet steer third revolution enhancing quality, reliability and repeatability in mass production (Industry 3.0).
We are on footstep of fourth industrial revolution (Industry 4.0) bringing new wave of connected manufacturing and smart factories. It is a combination of cyber – controlled, monitored physical systems (machines), complex automation and Internet of Things (IoT). Manufacturers worldwide are demanding to connect their factories (shop floors) to the nowadays cost-effective cloud environment and developing their own Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). This provides them opportunity to scratch untapped potential for exponential growth and bring ease of scalability.
Current Scenario
In a typical scenario, on shop floor, manually collected production data is entered into the system only at predetermined times such as at the end of a shift or job. The data is then made available in the form of reports and used for analysis. For long-term analysis, viewing the data “after the fact” is usually sufficient.
There are many opportunities for inaccuracies to creep into a manual data collection system. Often the data must be first written down, and later entered into the system – sometimes by a different person than the one that recorded it in the first place. Whenever a human operator enters data, he or she has influence over exactly what information is entered and when it is entered. The problem statement is,
- Manually collected data is not timely.
- Manually collected data is inaccurate.
- Manually collected data is biased
Smart Shop Floor
Technology that enables networked devices to exchange information and perform actions without assistance of humans.
- Now networking equipment with wired or wireless carriage have,
- dramatically decreased in cost, while
- Coverage, speed, and capacity have increased,
we can now embed connectivity into the “things” we use in our day-to-day lives. That translates to new business intelligence (BI), operational efficiencies, and revenue-generating opportunities.
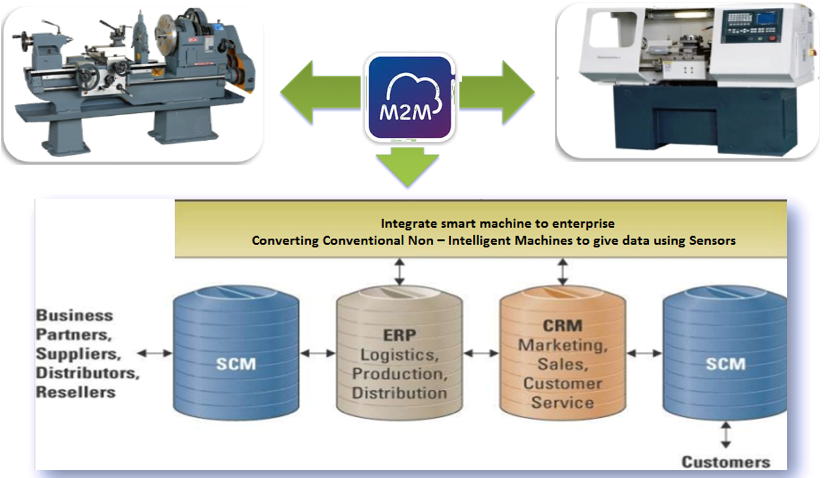
Digitizing manufacturing processes is a daunting task. Upgrading a manufacturing organization to Industry 4.0 can require a full-fledged paradigm shift – to impart organizational change and remolding existing processes. While machine-to-machine (M2M) and human-to-machine (H2M) connectivity are the major components of Industry 4.0, the real underlying benefit of Industry 4.0 resides in the machine-to-business connectivity, which is termed as “machine-as-a-service.”
“machine-as-a-service” comprehends a manufacturing machine’s roles to business goals through Industry 4.0. Today’s enterprises focus on how shop floor resources (machines) drive business revenue. Manufacturing companies no longer look manufacturing equipment as a one-time capital item purchase. The manufacturing equipment is costly items and nowadays the key performance indicators (KPIs) of the equipment are identified in advance and based on this machine’s output is monitored closely to see on how it contributes to revenue. Accordingly, the machines are partially financed based on the machine’s output. In essence, manufacturers do not just purchase the machine, but they also purchase a “subscription” to ensure that machine continues to drive and enhance the business, hence “machine-as-a-service”.
Service life cycle management is essential, as connected equipment requires maintenance on pre-defined intervals. However, service is no longer limited just to equipment maintenance and repair — service also entails to upgrades with enhanced features that enable your connected machine to support larger business goals, to give required business intelligence for more scientific inputs for raw material procurement, sales, productivity, CPI, etc.
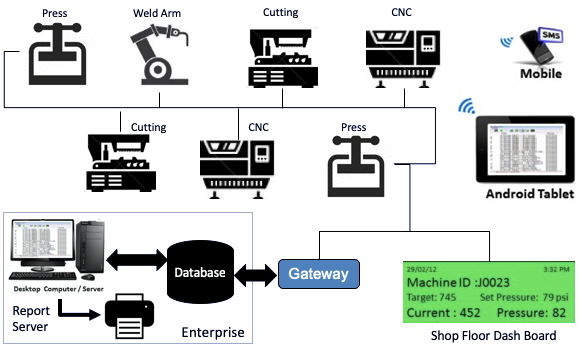
Machine – enterprise integration is essential for business intelligence. You Can’t Improve what you don’t measure. Sensors keep sending continued parametric data from machines to generate this business intelligence.
Business intelligence also aimed at reducing machine’s downtime and enhance productivity time besides streamlining raw material procurement, order processing and thus eliminating or minimizing waste in manufacturing process helping in ultimate objective of streamlining cash flow.
“machine-as-a-service” facilitates reporting feature that allows you to configure and generate reports on demand, or to set up schedules to automatically deliver pre-configured reports. The Standard Reports are templates that can be configured to include data from a specified time period, also from specific machines, operators, part numbers (or other important parameters depending on machine type), and/or shift. The individual reports have a number of report-specific configurable parameters called “filters” that control the report content.
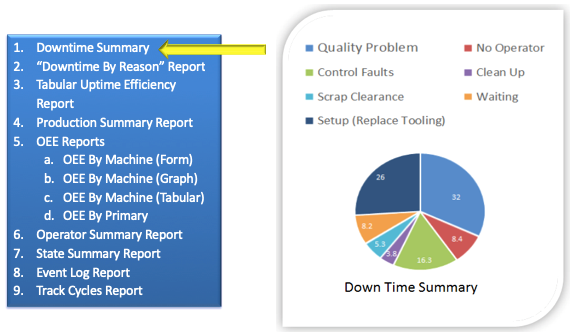
Above picture lists various reports depict to track Overall Equipment Efficiency. These reports help enterprise to optimize performance of major shop floor resource – “Machines”.
Summary
Smart shop floor, Industry 4.0 is all about generating the business intelligence for points listed below.
- Identifying potential areas of improvements.
- Making the most out of a limited amount of investment capital.
- Avoiding making inappropriate capital and material purchases.
- Freeing up capacity to diverse, compete.
- Decreasing run time costs through waste elimination.
- Shortening equipment ROI period through increased utilization.
- Reducing investigation time for root cause analysis.
- Directly tying production efficiencies to fiscal reporting.