Cyberattacks are rising at an alarming rate with technological advancements in this digital era. With cyber threats becoming increasingly frequent, safeguarding sensitive information has become one of the major concerns for organizations.
As the cyber threat landscape becomes more complex and an excessive lack of trained security professionals, several enterprises are exploring simplified ways to streamline the security operations. With the increase in the cybersecurity and staffing budgets, organizations are struggling to find appropriate solutions that can realize cost-effective security solutions at the required scale.
To combat these growing cyber threats, organizations are turning to security automation as a pivotal solution. Security automation can help your business safeguard valuable data better and more effectively than ever.
In this comprehensive guide, you will get to know what exactly automation security is, including how it works, the various types of tools available, and the significant benefits, among other things.
What is Security Automation?
Security automation is the process of using specialized software and tools to find, investigate, and address cyber threats automatically.
Additionally, security and automation basically include managing system configurations to ensure they are safe, automating scans, monitoring systems, generating reports, and responding to incidents.
Once these routine tasks are automated, organizations can minimize human error, get tasks done faster, and reduce the overall risk of security breaches.
Importance of Automation Security
Understanding what security automation might lead to think about why it is essential! These statistics will be eye-opening for you and might provide some valuable insights into the key problem areas.
- According to the IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report, the total cost of a data breach averaged $4.35 million. Depending on the size and financial stability of an organization, one cyberattacks could be enough to shut down the business entirely.
- Supply chain attacks are becoming more common, with Gartner predicting that 45% of global organizations will be affected by such an attack by 2025.
- Tracking the incident response times is an active way to understand if the cybersecurity is in step with the challenge. If the mean-time-to-detect and mean-time-to-remediate incidents are decelerating, then the current security device or procedure needs to be enhanced.
- If the security analysts or team are spending their time chasing down false positive alerts, this implies that they are wasting time and skillset in detecting false positives and fails to take appropriate security measures.
Now that you are aware of the key problems, here is the important role of security automation. A security automation solution is a unified software solution that can manage the security needs across entire organization in a holistic method. Some of the key capabilities of a security automation platform include
- Threat Detection: Identifies potential threats automatically to your organization’s systems.
- Alert Management: Improves and sorts alerts to speed up investigation processes.
- Automated Response: Executes predefined actions to manage and fix security issues with ease.
Also Read: Role of Cyber Security in Business Continuity
Types of Security Automation Tools
The rise of hunter-killer malware represents an evolution in cyber threats, requiring cybersecurity industries to adopt more proactive strategies. Traditional methods may fall short as these new malware types aim to undermine them directly.
With this in mind, let’s look at the various types of security automation tools.
1. SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response)
SOAR platforms integrate various security tools to streamline incident response, enabling faster detection and analysis. They help coordinate complex workflows, making your overall security system more effective.
2. SIEM (Security Information and Event Management)
SIEM technology collects data from all sorts of places, like your apps and devices. Then, it puts all this information together to alert you of any suspicious activity in real-time.
3. EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) and XDR (Extended Detection and Response)
EDR focuses on protecting individual endpoints like computers and mobile devices. XDR, on the other hand, offers a broader approach by covering EDR and network detection and response (NDR).
Both solutions use real-time response capabilities, machine learning-based detection, and other advanced features to help your organizations stay ahead of cyber threats.
4. RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
RPA tools automate routine tasks that don’t need complex analysis. Some security tasks RPA can handle include scanning for vulnerabilities, running monitoring tools and saving the results, and basic threat mitigation.
Core Processes of Security Automation
While different security operation tools automate differently, most of them follow a typical process. Here is an outline of the typical security automation processes.
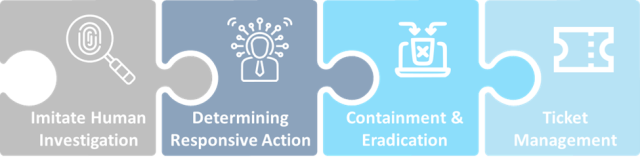
Step 1: Imitate Human Investigation
- Receives notifications from various security tools.
- Correlates these alerts with other data or threat intelligence to determine whether an alert indicates a real security incident.
Step 2: Determining Responsive Action
It identifies the type of security incident and accordingly selects the appropriate automated response.
Step 3: Containment and Eradication
Performs automated actions to prevent the threat from spreading and to remove it from affected systems. A few examples of the automated actions are as follows.
- Automatically isolate an infected device from the network to prevent further damage.
- Move suspicious files to secure areas where no further harm can be caused.
- Automatically uses antivirus software to remove malware.
Step 4: Ticket Management
- Automated systems use rules to assess whether automated actions were successful in addressing the threat.
- If further action is needed, they can integrate with on-call systems to alert human analysts with more detailed information.
- On the other hand, if no further action is required, automation can close the ticket and provide a detailed report on the threat and the actions taken.
What Security Processes Can Be Automated?
Now that you know about the processes of security automation, it is essential to understand what specific security processes can be automated. Read on to find out!
| Security Process | How Does Automation Help? |
| Threat Hunting | Speeds up threat detection without manual intervention in complex IT environments. |
| Security Incident Response | Makes it easier and faster to detect threats quickly and respond to incidents efficiently. |
| Endpoint Protection (EPP) | Automated solutions quickly detect, investigate, and address threats on endpoint devices. |
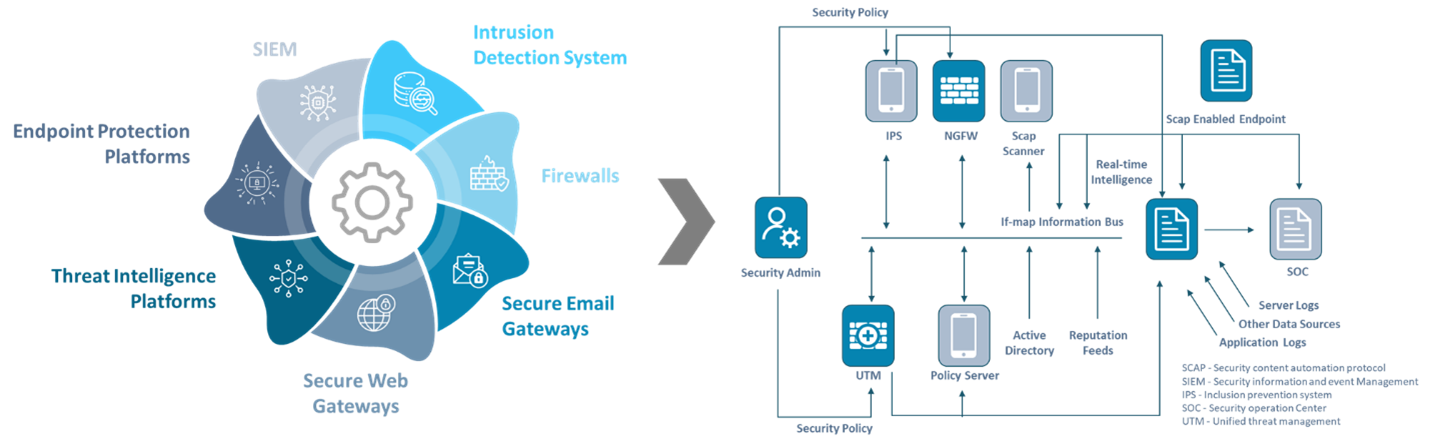
The following image depicts the reference security architecture and the key features in security automation.
Security Automation Use Cases
Here are several use cases that can help to make an informed decision.
| Use Case | Description |
| Automatic Endpoint Scans |
|
| Automatic Testing Code Generation |
|
| Security Automation Rule Updates |
|
How to Successfully Implement Automation Security?
Now that you have learned about the process and use case of automation security, it’s time to focus on the next crucial step: implementing automation security.
Follow these steps to implement automation security in your organization successfully.
Identify Your Needs
It is important to determine how security automation can address your organization’s specific needs. For instance, tool requirements and processes may be different for different industries across retail, healthcare, or finance. It is also essential to understand industry challenges.
Consult with Your Team
Discuss with your IT team and other key stakeholders to identify the problems you need to solve.
Here are some key questions you must consider.
- How many alerts are received and handled each day by your security team?
- What are your time threats that remain undetected, and what are the response times?
- Which tasks are repetitive and well-defined, and how can automation improve these processes?
Define Use Cases
Create a list of use cases based on your industry needs and organizational goals. This is a critical step for researching vendors, so spend time on research in this phase.
Here is an example highlighting a few use cases for the healthcare industry to help you better understand how to define use cases effectively.
- Automated patient data protection to prevent unauthorized breaches.
- Continuously scan for potential threats in patient management systems for real-time threat detection.
Study the Providers
Here are a few things to consider when looking for providers.
- Select tools that require minimal or no coding to deploy and create playbooks.
- Ensure the solution supports integration with your existing tools.
- Choose a cloud-based solution for easier maintenance and flexibility.
- Discuss with vendors the time required for full deployment.
Benefits of Security Automation
Here are the top 5 benefits of security automation.
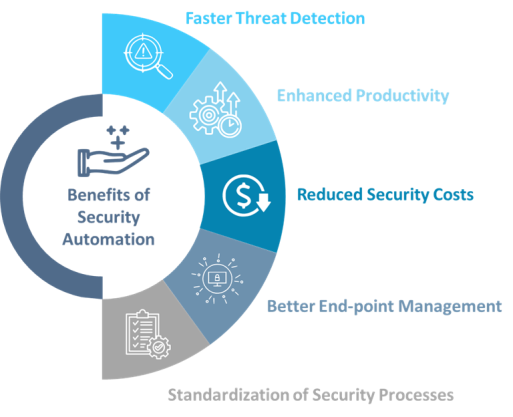
Faster Threat Detection
Security Operation Centers (SOC) get lots of alerts throughout the day and are unable to investigate every incident properly. In such cases, automation can help in quickly sorting these alerts to identify real incidents. This, in turn, allows SOC analysts to address threats more efficiently.
Improved Productivity
Moving manual tasks to automation allows analysts to focus on more complex issues and increases overall productivity. Not only this, but security automation also enables Level 1 analysts to handle a broader range of tasks without escalating issues to more skilled staff.
Standardization of Security Processes
Using security automation requires a consistent set of security tools across the organization. This makes it easier to automate tasks and ensures that manual processes are clearly defined and applied consistently.
Reduced Security Costs
Security automation lowers your security costs by automating repetitive tasks and streamlining workflows. This reduces the need for specialized staff as automation tools can manage them effectively.
Better Endpoint Management
Endpoints, often seen as the “doors and windows” of a network, can become entry points for attackers if not properly protected. Hence, having real-time visibility and securing endpoints by streamlining updates, monitoring, and vulnerability resolution is one of the most crucial benefits of automation security.
Challenges Addressed by Security Automation
Organizations face numerous significant challenges when relying on traditional security systems. Security automation can address the following changes effectively.
| Challenge | Description | How Does Automation Security Help? |
| Time-Consuming Manual Security Processes | Manual methods struggle with the volume and complexity of security alerts. | Automates alert and response, reducing manual effort and minimizing errors, thus improving threat detection. |
| Poor Visibility Increased Costs | Many traditional tools operate in silos, causing redundancies and inefficiencies. | Streamlines security workflows, providing a unified view and reducing costs. |
| Complexity in Compliance Management | Maintaining compliance can be complex and labor-intensive. | Automates compliance monitoring and documentation and ensures up-to-date controls. |
Best Practices for Implementing Security Automation
All set to implement security automation technology in your organization. Here are a few best practices you must keep in mind.
Prioritize Automation
- Identify the most frequent and time-consuming security threats.
- Then, you must define use cases where automation can be beneficial based on your set organizational goals.
Manual Playbooks
- Begin with manual playbooks and document current steps, processes, and best practices used to handle security incidents.
- Use these playbooks to automate the most repetitive and time-consuming tasks and ensure that your team follows a consistent process whenever an incident occurs.
Adopt Automation Gradually
- Start with tasks that are easiest to automate and offer immediate value.
- Implement automation in phases so that you can monitor progress and adjust as needed.
Invest in Training
- It is essential to educate staff on how to use automation tools effectively.
- Train them on the processes to set up, handle, and escalate tasks from automated systems. Here is how you can ensure that your team is well-trained.
- Clearly highlight the tasks which need to be automated.
- Train staff on how to shoot up issues to human analysts when needed.
- Use practice scenarios to build confidence.
Conclusion
Automation security tools have become indispensable for staying ahead of rapidly evolving cyber threats. In an era where cyber-attacks are so frequent and where there is a shortage of skilled security professionals, security automation is the only way to go forward. Every business is different when it comes to securing their digital assets. Calsoft’s security solutions and specialist consultants help customers with not just evaluating ‘detect and respond’ capabilities for their technologies, people, and processes, but also AI/ML-based cybersecurity prevention solutions.






