Introduction
In today’s world, there are several options where data can be stored. Organizations choose options that are swift and cost-effective to get the most out of existing infrastructure and have a parallel focus on developing new, customer-focused capabilities. The organizations aim is always to have secure, accessible and affordable solutions. Two such solutions are cloud computing solutions and on-premises solutions.
In this blog, I will try to give you a comprehensive overview of on-premises versus cloud solutions and also write about the hybrid cloud solutions.
What is Cloud?
Cloud computing, is all about working with applications, data, and programs over the internet instead of having them locally. The cloud is just a metaphor for the Internet. Organizations choose to implement Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), where the organization subscribes to an application it accesses over the Internet (Think Google Apps), then there is Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), where the organization can create its own custom applications for use by all in the company (Think Windows Azure) and finally there is something called Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), where big players provide a backbone that can be “rented out” by smaller organizations (Think Amazon, Rackspace etc.)
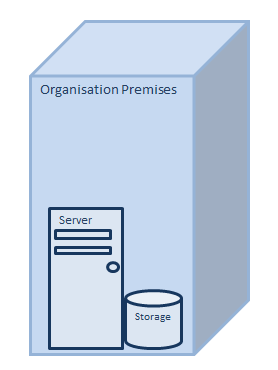
What is On-Premises Cloud?
On-premises or On-prem, means working with applications, data, and programs operating on the company’s in- house server and computing infrastructure. The company is responsible for the security, availability and overall management.
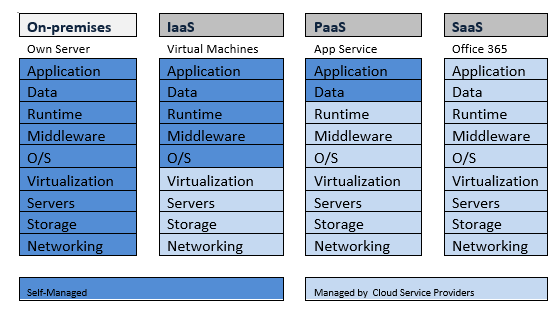
Summary of On-Premises and Cloud options
In the following section, I have captured the summary of cloud options and on-premises
Comparison of Cloud and On-Premises
| Cloud | On-premises | |
| Setup |
|
|
| Scalability | Can be easily scaled to meet demand. | Scaling-up requires an additional purchase of equipment. |
| Ongoing costs | Pay as you go, If servers are not needed, there is no cost. No cost required for power consumption of servers or to maintain them | Have to pay the cost of maintenance, upgrades, and energy usage and hardware replacement. |
| Customization | Typically configurable but depending on how it is hosted by the cloud provider. | Complete control over hardware, an organization can decide on the configuration, the upgrades and system changes. |
| Total Cost of Ownership | Although requiring a lower upfront investment, cloud applications can be more costly over the course of the system’s life cycle, increasing total cost of ownership (TCO) | Since you are only paying for your user licenses once, an on-premise solution can have a lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) |
| Connectivity/Uptime | Cloud solutions require reliable internet access for you to remain productive. | With on-premise systems, you do not rely on internet connectivity or external factors to access your software. |
Which is the best option for an organization?
The fact is both these approaches are unique in their own way and have their own pros and cons. At the end of the day there is no black and white answer it all depends on the needs and the requirements of the organization. The choice has to be made based on what works best with your current architecture.
Hybrid Solution
With all of this data in hand, an organization can take the decision to choose between cloud and on-premises based on what suits the organization’s requirements. Since both solutions have advantages and disadvantages, there are lots of organizations coming up with the hybrid solutions. Basically, hybrid cloud means managing a public and a private cloud as one, or at least being able to have management tools across the two environments. There are many types of hybrid cloud solutions.
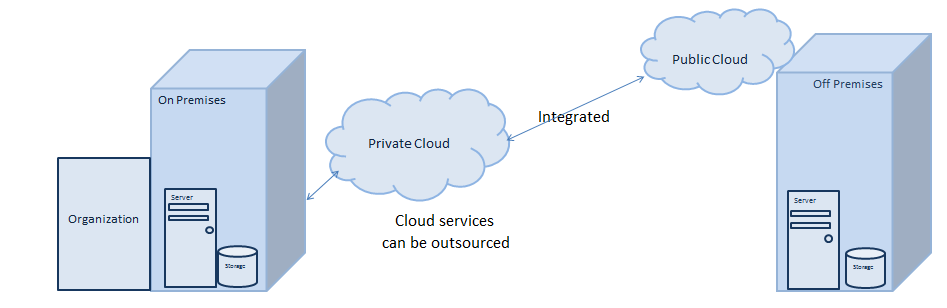
In a hybrid solution, the computing environment combines a public cloud and a private cloud by allowing data and applications to be shared between them. There are several ways in which a hybrid solution can be achieved, one such method is where organizations who manage their private clouds themselves sign up to a public cloud and then can be integrated into their own infrastructure.
In the above example of a hybrid solution, the organization has a Private cloud where the IT infrastructure is provisioned on-premises and is managed internally. The cloud services are obtained by the cloud service provider’s i.e. the private cloud is integrated with the public cloud. The public cloud will provide the management options available by the cloud provider on the on-premises infrastructure.
In this solution, the security threat of data being on public cloud with other organization is solved and all data remains on-premises and also the organization can utilize the features from the cloud provider.
Which solution is right for your organization?
[Tweet “On-Premises versus Cloud Solutions ~ via @CalsoftInc”]