Kubernetes is a container orchestration engine that was originally designed by Google
(Google has been using it for 10 years) and is now maintained by Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF). It has been used to run Google’s massive systems. Kubernetes is also described as a vendor-agnostic cluster and container management tool, open-sourced by Google in 2014. Since 4 years is when Kubernetes was pushed into open source. It provides a layer of infrastructure that allows management of applications with different services as a single application and also manages containerized applications in a clustered environment.
Container, by definition, is a pack of code plus its dependencies, and can be run anywhere. It’s like a mini-virtual machine that does not have device drivers and other components of a regular virtual machine. Before containers became popular, virtual machines were the most popular technology to allow a single server to run lots of different applications that were isolated from each other. Docker is the most popular container written in Linux.
Container orchestration with Kubernetes
As public and private clouds are evolving, everyone is looking to build applications for cloud architectures. This cloud native applications follow an IT trend where development and deployment should be at scale and cost-efficient. This is mostly achieved by leveraging cloud services to get run-time platform capabilities such as performance, scalability and security out of the box. These cloud native applications need lot of management for scalability, resilience, monitoring. Kubernetes (k8s) from Google has become the de-facto standard for orchestration of container based deployment which can be on-prem or on cloud. It helps assign containers to machines in a scalable way, keep them running in the face of failures and facilitating them talking to each other.
Kubernetes architecture consists of a cluster which has master nodes and slave nodes, which makes it easy to deploy in public clouds. Kubernetes integrates with clouds to utilize storage volume and load balancing services. By deploying Kubernetes on the Cloud, we can take advantage of the functionality of Kubernetes along with the flexibility and security of cloud services. In order to run loosely coupled services on this cluster infrastructure, there has to be strong networking between the nodes, effectively the pods. The services running inside Kubernetes (kubenet, kubeproxy) take care of networking aspects of IP addresses, DNS, iptables firewall policies. To understand pod networking, you will have to play with network namespaces which is one of the building blocks of containers. Fortunately, Kubernetes provides a CNI (container network interface) plugin based architecture to take care of networking.
CNI plugin provides network interface which connects to container network namespace and make necessary changes to host. These plugins take care of basic networking features like IPAM, Routing, DNS as well as designing networking features for overlay networks using various tunneling technologies.
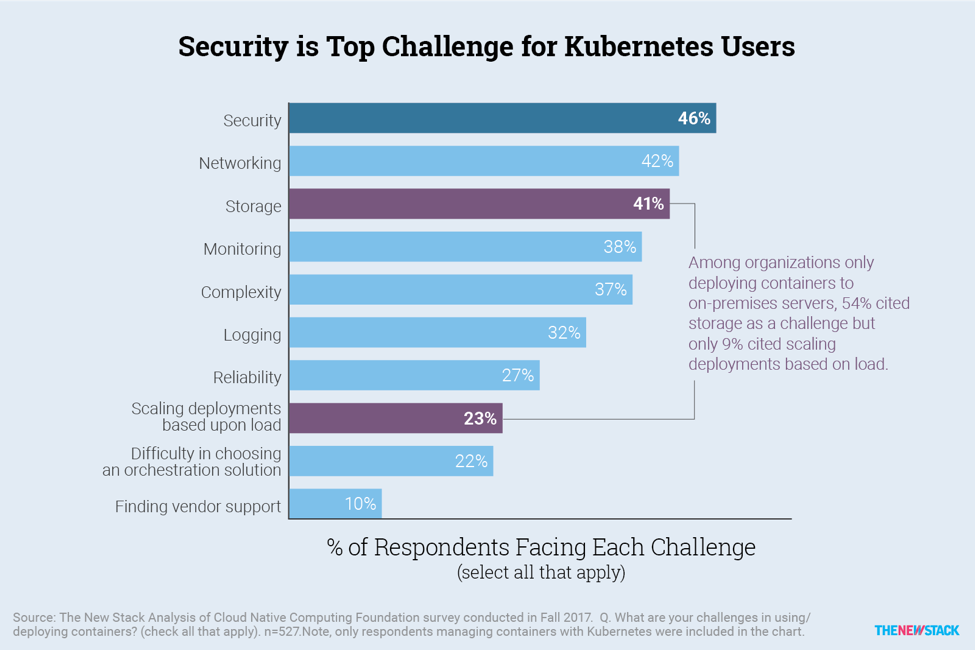
Deployment challenges faced by Kubernetes users
Using or deploying Kubernetes unveils certain challenges. Some challenges are unique to Kubernetes, while other trace back to adoption challenges.
While Security factors take the lead, networking and storage coming challenges settled in the second and third place.
Security, Storage, Networking Among Top Challenges
(Source: https://thenewstack.io/top-challenges-kubernetes-users-face-deployment/)
[Tweet “Kubernetes and the Containers – A look under the Hood ~ via @CalsoftInc”]