The merger of software and networking is one of the primary factors for radical developments in the modern networking approach. Software-defined networking (SDN) and virtualization are redefining the way network infrastructures are managed and architected. Focused on delivering enhanced flexibility, efficiency, and scalability, these technologies are establishing a foundation for newer innovations. One such revolution in this genre is SDN, which is a method of network administration and is gaining traction. On the other hand, Virtualization is a significant concept that rewired traditional network designs and at the same time is the heart of SDN.
In recent times, SDN and virtualization have emerged as transformative forces, radically changing how network infra is architected and managed. These technologies are indeed ground-breaking. One such innovation in this realm is VMware’s NSX series—a pioneer in network virtualization. However, to optimize their NSX-based network infrastructure effectively, organizations must maintain a proactive approach in staying informed about the latest happenings in the NSX realm.
What is the primary need to upgrade from NSX-V to NSX-T is one of the most common questions for enterprises that leverage VMware’s NSX virtual network solution. The software-defined networking model is one of the most popular and widely used as it has all the features necessary to build complex network configurations. Today, as organizations sort to modernize their infrastructure and cater to changing demands, the move from NSX-V to NSX-T becomes pivotal. Not just this, since VMware is closing on the tech support for NSX-V, it has become more important to move base to its successor called NSX-T which comes with an array of improvements. However, it requires a comprehensive understanding of the difference between the two tech platforms before enterprises embark on the migration journey. Let us now explore NSX-V and NXS-T, and the key differentiating factors between the two.
Brief understanding of NSX-V and NSX-T
VMware NSX is a ground-breaking network virtualization platform that leads organizations to move their networking operations to the cloud. It is a solution that enables building a cloud smart network with networking and security to get on track with consistent policy, operations, and automation across multiple cloud environments.
The image below gives a brief understanding of the overall NSX architecture.
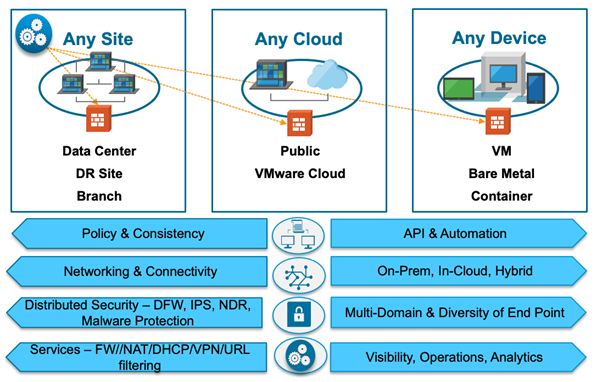
How does NSX work?
VMware’s NSX gains end-to-end network virtualization by leveraging network encapsulation. This process requires wrapping network traffic within protocols that traditional physical networking hardware supports, such as Generic Routing Encapsulation. Further, it divides physical networks into independent virtual networks, discarding the need for bank-breaking in-house equipment. At the core of the VMware NSX series is the NSX Data center that works towards virtualizing networking elements like VPNs, firewalls, and load balancers. As an extension to these components, VMware NSX is engineered to streamline networking and improve overall performance.
VMware’s NSX-V – for vSphere is one of the flagship platforms for network virtualization within VMware environments. However, with the release of NSX-T i.e. Transformers, VMware has introduced a next-gen solution tailored to the diverse needs of modern data centers and multi-cloud environments.
Understanding the Transition and the Need to Migrate
Before getting to the details of the topic, it is important to understand the rationale behind NSX-V to NSX-T migration. While NSX-V is a pro in virtual cloud networks such as data centers, application frameworks, and cloud, NSX-T extends its reach to include containerized workloads, hybrid or multi-cloud infrastructures, and multi-hypervisor environments. This extension of scope enables NSX-T to be a more versatile solution capable of accommodating diverse deployment scenarios.
Several reasons can support your decision to migrate from the NSX-V to the NSX-T platform. Here is a sneak peek into some important ones:
- End of support
- Enhanced security features in the next version
- API-driven approach to support automated deployments
- Improved speed to market
- Supportability
NSX-V & NSX-T: Key Differentiating Factors
Overview of VMware NSX Technology
Architecture
NSX-V runs on the VMware vSphere environment, tightly integrated with vCenter and ESXi hosts. In contrast, NSX-T possesses a decoupled architecture and delivers greater flexibility by supporting multiple hypervisors, Kubernetes, and bare-metal deployments.
Networking Models
NSX-V follows a traditional networking model, leveraging constructs like VXLAN for overlay networking. NSX-T introduces a more abstract approach with the Geneve protocol, facilitating enhanced scalability and interoperability across heterogeneous environments.
Security Features
While both platforms prioritize security, NSX-T introduces native support for micro-segmentation across a broader spectrum of environments, including containers and bare-metal workloads. Its distributed firewall capabilities offer granular control and visibility, empowering organizations to fortify their defenses in multi-cloud scenarios.
Automation and Orchestration
NSX-T focuses on streamlining automation via DevOps. Engineered to run effortlessly with modern infrastructure-as-code, works toward making tasks more automated and flexible.
With its API-driven setup, it easily fits into automation tools and orchestration systems, making networking simpler and more adaptable to changing needs.
Operational Considerations
Transitioning from NSX-V to NSX-T requires careful planning and a good idea of operational implications. While NSX-T offers enhanced flexibility and scalability, migration involves rearchitecting certain set of components and workflows to align with the new pattern. This is the primary reason why end-to-end testing must be undertaken to avoid issues in the transition without disturbing critical business operations.
Now that we have a fair idea about the differences between the two platforms, let’s understand what you need to know before embarking on the migration journey.
Assessment and Planning
This is the first step which focuses on conducting a comprehensive assessment of existing infrastructure and workloads to take note of dependencies and compatibility requirements. Post which a migration plan can be developed tailored to the organization’s unique needs, covering phased migration approaches along with rollback strategies.
Pilot Deployment
Initiate a pilot deployment to validate the migration process and assess the performance and compatibility of NSX-T within the target environment. Leverage testing and validation tools to mitigate risks and refine migration procedures before full-scale deployment.
Incremental Migration
Next up, go for an incremental migration approach to reduce disruption and be prepared to mitigate potential risks. Begin with low-impact workloads and progressively transition critical applications and services to NSX-T. Do not forget to closely monitor the performance and functionality throughout the process.
Training and Knowledge Transfer
To have a streamlined migration, it is mission-critical to educate and equip IT teams with the necessary skills and expertise to effectively manage and operate NSX-T environments. Provide comprehensive training and knowledge transfer sessions to ensure seamless adoption and optimize the benefits of the new platform.
The table below briefly segregates the features of NSX-V and NSX-T for a better understanding.
| Feature Comparison | NSX-V | NSX-T |
| Basic Functions | Offers premium features like deployment reconfiguration, rapid provisioning, and destruction of any given on-demand virtual network.
Allowing a single virtual switch to connect to multiple hosts in a cluster by leveraging the vSphere distributed switch. |
Offers users with agile software-defined infrastructure, suitable for developing cloud-native application environs.
Comes with built-in support for multiple clouds, multi-hypervisor environments, and bare-metal workloads. |
| Origin | Released in 2012, NSX-V is built around a VMware sphere environment. | Even though NSX-T originates from the vSphere ecosystem, it is built from scratch and designed to address some of the use cases not covered by NSX-V. |
| Hypervisor Support | vSphere virtualization is supported by the stack. | Along with vSphere, NSX-T supports Docker, Kubernetes, OpenStack etc. |
| Migration | Migration from NSX-T to NSX-V is not possible. | NSX-T manager has a built-in utility for users who wish to move from NSX-V to NSX-T. |
| Deployment | Deployment of ESXi VM is possible. | Acting as an individual solution it can be deployed as an ESXi or KVM VM. |
NSX-V and NSX-T overall are different from each other in various ways. However, transferring from NSX-V to NSX-T requires careful planning, with considerations for assessment, pilot deployment, incremental migration, and training. It is equally crucial to sign up for end-to-end testing and deliver comprehensive training to stakeholders to make sure the migration process is smooth, increasing the benefits of the new platform.
Read our Ultimate Guide for NSX V to NSX T Migration to plan for your upcoming NSX-V to NSX-T migration in the most strategic manner.
Conclusion
As enterprises are in the race to digital transformation, moving base from NSX-V to NSX-T platform is a great leap toward modernizing network infrastructure and witnessing the agility of software-defined networking. By understanding the key differentiators between the two platforms and adopting a strategic migration approach, organizations can look forward to newer opportunities for innovation and growth in a dynamic environment.
Calsoft has been a VMware partner for 23 years and was recently honored as the official Broadcom-VMware vendor, bringing immense experience and expertise in the NSX platform at large, and can be your trusted ally for NSX-V to NSX – T migration.






