Executive Overview
Over the years, business entities have setup their IT infrastructure using high end Hardware and custom built applications. Beyond a point, this infrastructure cannot be scaled to meet the challenges of growing business needs. Professional cloud service providers offer cheaper and better options which can be leveraged to meet growing business need. Organizations cannot simply discard their huge investments in their IT infrastructure to move to cheaper options. Security and compliance issues prohibit moving applications running on their on-premise data center to Public Data center. Due to all of these prohibitions, Hybrid cloud model is the answer. It can leverage existing IT infrastructure (private cloud) and scalability of public cloud to offer a scalable & robust data center.
Use Case for Hybrid Cloud
A Pharmaceutical company may store sensitive medical history of patients at their in-house private cloud. Application on public cloud may use this sensitive data as an input for business analytics. This explains how enterprise can utilize capabilities of hybrid cloud to deliver a specific business requirement.
The purpose of the blog is to discuss the steps involved in deployment and implementation of hybrid cloud for an enterprise.
What is Hybrid Cloud
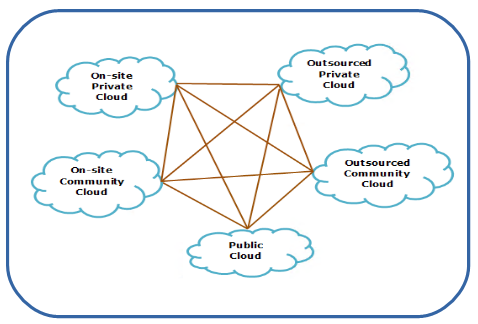
Hybrid cloud is a mix of two or multiple clouds in any format – private, community, or public that operate as unique entities but allows for data and application portability and are bound together by standardized or proprietary technology.
Private and community cloud can be setup in two ways, on-site and outsourced. Different constituents (private, community and public) are bound by standard protocols. Within hybrid cloud, constituents maintain their distinct identity and applications running on them are secured. However, it allows data and application portability via standard industry protocol.
Hybrid cloud can include and utilize resources from different cloud service models such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS). Simple view of hybrid cloud using different cloud deployment models.
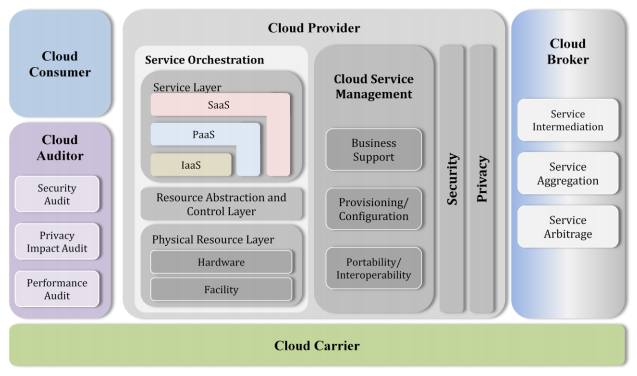
Cloud Computing Reference Architecture
Below diagram depicts a high-level reference architecture of cloud landscape. It shows all components involved in any cloud computing ecosystem (Source: NIST cloud computing reference architecture).
Understanding each component of this reference architecture is important for successful deployment and implementation of cloud infrastructure. NIST reference architecture defines five major players:
- Cloud consumer: person or organization who consumes cloud services
- Cloud provider: cloud service provider such as AWS, Azure, BlueMix, Google etc
- Cloud carrier: Intermediary that provides connectivity of cloud services from cloud providers to cloud consumers through network.
- Cloud auditor: Person or organization doing independent assessment of cloud services, operations, performance and security of the cloud implementation
- Cloud broker: Person or organization providing services of service intermediation, service aggregation, and service arbitrage.
Cloud Implementation
Enterprises who want to adopt and deploy hybrid cloud in their data center have to prepare themselves for this new paradigm in IT infrastructure. Understanding business value of hybrid cloud and use cases where it can be leveraged is the first step to hybrid cloud computing. Key factors such as costing, security, locality, service levels, system independence and service portfolio have to be taken into consideration. The next step is to develop cloud readiness checklist considering all aspects of the organization. Following are key considerations for implementing a hybrid cloud in any organization (Source: Cloud Standard Customer Council):
- How to determine the placement of solution components.
- How to integrate with existing enterprise systems.
- How to handle an increase of management complexity.
- How to ensure that security is considered in all aspects of the hybrid cloud.
- How to deal with rapidly evolving and partially mature technologies.
- How to implement common operational services such as backup and disaster recovery in a hybrid cloud.
- How to ensure adherence to regulatory and compliance requirements.
There are two generic methods for adoption and deployment of Cloud infrastructure:
- Prescriptive method: It consists of prescribing solutions for future opportunity and it mitigates a future risk and illustrates the implication of each decision option.
- Evaluative method: Mostly used for SaaS adoption. It consists of a set of analysis techniques which compares existing applications with SaaS applications on factors such as business values and features available. This aids the decision making of enterprise before adopting any solution.
Options from multiple cloud service providers are available in the market. They provide all types of cloud service, IaaS, PaaS and SaaS. Major services provider are:
- AWS
- Microsoft Cloud Solutions
- Redhat Openstack Cloud solutions
- VMware Solutions
- Open Source solutions such as CloudFoundry.
Enterprise can select any option to suit their need of existing applications in their data center.
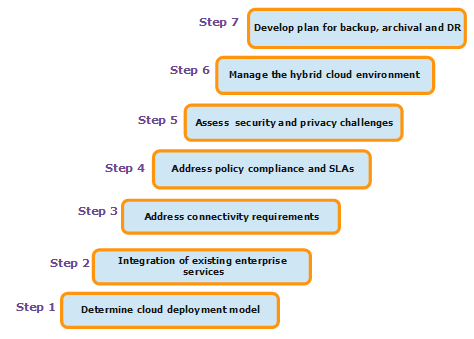
Prescriptive guidance for Hybrid Cloud implementation
Cloud implementation in an organization depends on size of the organization and its IT maturity level. The cloud eco-system is huge and complex. Below diagram depicts prescriptive steps to perform for successful implementation of hybrid cloud infrastructure for an organization.
Each step mentioned in above diagram is a big exercise in itself. Explaining each step here is out of scope for this article. There are many cloud service providers who provide a wide variety of services for each layer.
There is no one-size-fits-all solution for hybrid cloud. Customers need to exercise due diligence to before deploying a suitable Hybrid cloud infrastructure for their business. Proper planning is required to develop a hybrid cloud deployment model. Identifying and selecting the right resource model at the beginning itself is important. Course correction at later stage can be disruptive.
References:
http://www.cloud-council.org/deliverables/CSCC-Practical-Guide-to-Hybrid-Cloud-Computing.pdf
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn568099.aspx
HP: iSpeak Cloud™: Embracing Digital Transformation
[Tweet “Deployment and Implementation of Hybrid Cloud for an Enterprises ~ via @CalsoftInc”]