Before understanding what is Blockchain we should be clear that Blockchain is not Bitcoin (digital money) it is so much bigger than that, it is not Regulated and difficult to comprehend.
Blockchain is now what internet was in 1990s
Many sources have defined Blockchain as a ‘distributed, decentralised transaction ledger’ and it also is immutable, resilient and secure. Blockchain makes things Transparent, Democratic, Decentralized, Efficient, and secure.
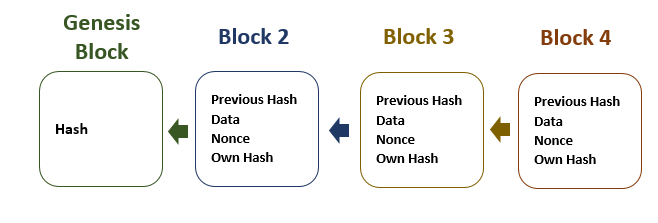
Blockchain is a ledger of records arranged in data batches called blocks that use cryptographic validation to link themselves together.
A brief Cryptography background
- Cryptography is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication.
- Hashing- A hash value is a numeric value, of a fixed length, that uniquely identifies some data.
Hash looks like – e0d123e5f316bef78bfdf5a008837577 - Nonce is a number generated for a specific use, such as block generation, to be used only once.
Each block references and identifies the previous block’s hash forming an unbroken chain.
Components of Blockchain
Blockchain mechanism?
Blockchain is a technology that enables moving digital coins or assets from one individual to another. If person A transfers Money to person B, a 3rd party is involved in the process and the money will be transferred from anywhere to everywhere in the world. But the transaction will take some time and money to get executed.
What blockchain attempts to address is the deletion of 3rd Party money transfer. With the help of this technology, transfers can be done immediately and in a much cheaper way.
Transfer of money between 2 parties is recorded in a ledger. Suppose Person A transfers $10 to Person B and Person B transfers $ 8 to person C and person C transfers $5 to person D, It is a chain of transactions that is visible to everyone. Everyone in the network can track where the money is and how much money each one has had and everyone can decide whether the transaction is valid or not valid. Any invalid transaction will not be the part of chain.
Every participant will have the copy of the ledger and all the copies will be synced so everyone will see the same records.
Process of Confirmation
One of the most important aspects of blockchain technology is the way that it confirms and validates transactions. In the example above three individuals conducted transactions online, each with a private and a public key. Blockchain allows the first person (person A) to use his private key to attach information regarding the transaction to the public key of the second person (person B) which holds true person for all transactions ahead. Such package of information together forms part of a block, which contains a digital signature as well as a timestamp and other relevant information about the transaction, but leaves out the identities of individuals involved in that transaction. These blocks are then transmitted across the blockchain network to all the nodes, or other components of the network, which act as validators for the transaction.
Industries – Blockchain will penetrate:
- Banking and payment
- Cyber Security
- Supply Chain Management
- Forecasting
- Insurance
- Transport
- Online data Storage
- Charity
- Voting
- Government
- Public benefits
- Healthcare
- Energy Management
- Online Music
- Retail
- Real Estate
- Crowdfunding
Important points:
- A Blockchain is a type of ledger that records transactions
- If a transaction is approved by a majority of nodes then it is written into a block
- Each block generates a hash
- A hash is alphanumeric string
- Blocks are entered in the order in which they occurred
- Even a small change in a transaction creates a completely new block with a new hash
- Each block refers to the previous block and together make the Blockchain
- A Blockchain is effective as it is spread over many computers, each of which have a copy of the Blockchain
- These computers are called nodes
- The nodes check to make sure a block has not been changed by inspecting the hash
- The Blockchain updates itself every 10 minutes
[Tweet “Blockchain – Blocks the Chain of Agents ~ via @CalsoftInc”]