Introduction
Network functions virtualization (NFV) refers to specialized network services traditionally run on proprietary, dedicated hardware. Functions like routing, firewalls and load balancing are packaged as virtual machines (VMs) using NFV on commodity hardware.
At present, general purpose network processors are used to implement NFV. It is known to be a challenge to implement NFV on standard computing platforms using virtualization. Cloud companies have realized this and have investigated other types of technologies and techniques, resulting in the adoption of containers and DevOps models as well as FPGA-based reconfigurable computing.
FPGAs and Network Processing
FPGAs (Field Programmable Gate Array) have traditionally been a part of network processing. Reconfigurable logic has been used for both wired and wireless communication. FPGAs are used to speed up processing of network packets for variety of network functions/ applications like Intrusion detection, firewall, packet parsing, content based switching, IP lookup, deep packet inspection, etc.
FPGAs can be programmed both statically and dynamically. Static reconfiguration means that the whole FPGA is stopped and configured with a new configuration file. FPGAs were mainly configured at design time and when a new upgrade was available for the specific application in most of the industrial network applications.
In dynamic configuration, part of FPGA can be reconfigured while rest of the FPGA continues to operate without any pause or delay. This is used for designing systems that can adapt to processing requirements. Hardware accelerator units can be dynamically changed to manage network traffic fluctuations. More specifically, a network processing platform can dynamically reconfigure number of compressions and encryption hardware acceleration units to meet the processing requirements of the network traffic.
FPGA based Network Function Virtualization
Many chip manufacturers and hardware integrators have brought up programmable platforms based on specialized network processors. This induces fast paced development of specialized dynamically reconfigurable network applications.
Napatech brought FPGA based NICs. Marvell offers Xelerated processor for fiber access application as their so called Metro Ethernet Application. Xilinx has released the SDNet approach which supports SDN functionality through programmable data plane hardware.
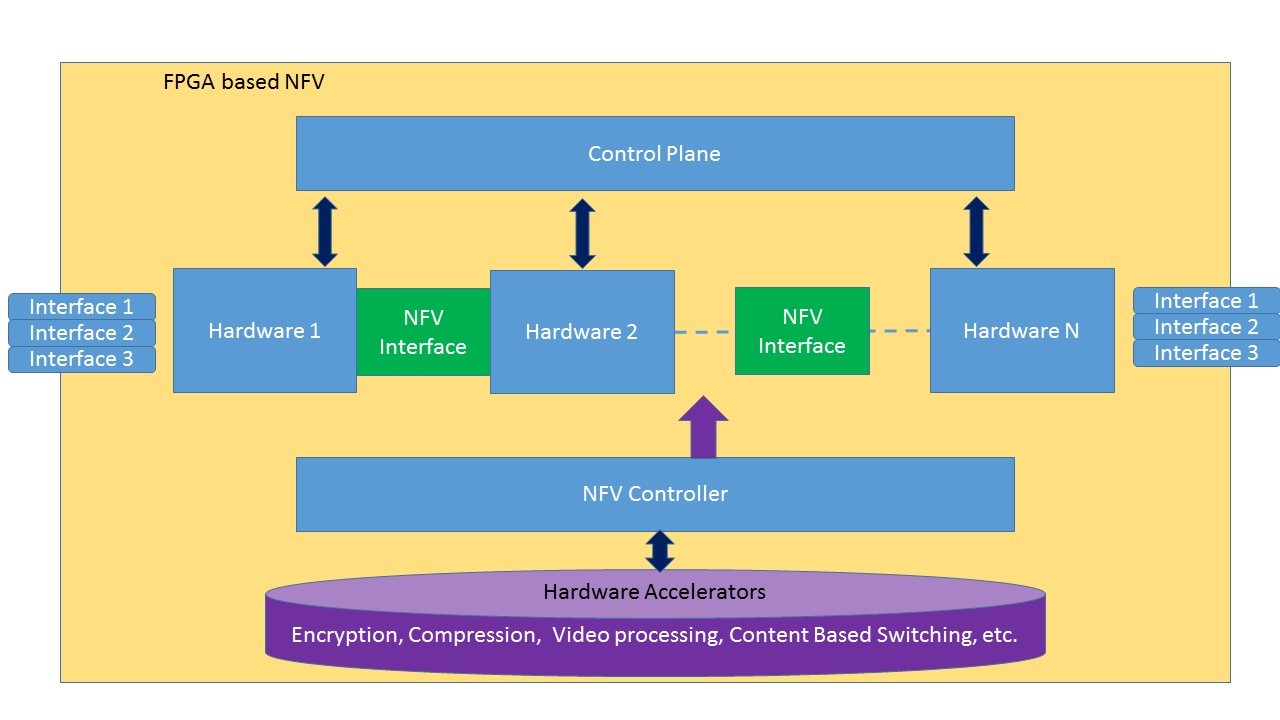
NFV provisions flexibility and fast deployment of software-solutions and also provides high throughput of specialized hardware devices, using FPGAs as the main hardware.
The above figure depicts FPGA based NFV architecture. In it, FPGAs use hardware libraries of hardware components for configuration of specific application. The major advantage of this is it creates ecosystem of FPGA manufacturers and system integrators along with IP block vendors. It provides higher flexibility, and high innovation scope for yielding maximum throughput. NFV interface provisions inter-operability of hardware components from different vendors. The NFV controller can be used to load the components from the library, program the FPGA and then configure the modules based on the application’s requirements through the NFV-Configuration Interface.
NFV controller can load the required modules from the hardware accelerator library to support network encryption and network compression using the FPGA-based NFV framework. Due to traffic fluctuations, if the number of network flows that need encryption increases and the number of flows that need compression reduces, then, the NFV-controller can program the FPGA with additional modules for encryption (or with more efficient modules for encryption that allocate more area). Thus, the FPGA-based NFV can adapt its resources based on the network traffic fluctuations. In applications where we need both a high degree of flexibility and also a high degree of performance, FPGA-based NFV platform can be used as a promising platform.
Reference
[Tweet “Achieving Better NFV Performance & Flexibility with FPGA-Based Platform ~ via @CalsoftInc”]






