5G technology rollout signifies an immense revenue opportunity for the telecom industry. 5G technology and its capabilities have immense potential to become the primary standard for the telecom industry, steering an innovative era of ultra-reliable connectivity, coverage, and speed. 5G can connect businesses and individuals on a huge scale. The telecom industry is witnessing a rise in latency-sensitive and high data rate applications. As specified in the International Mobile Telecommunications – 2020 (IMT 2020), 5G supports complex services relating to diverse use cases such as enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), massive Machine Type Communication (mMTC), and Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (uRLLC). However, to deliver these novel business models, Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) face significant challenges with the current infrastructure.
Network transformation is required from traditional monolithic networks, lacking flexibility, scalability, and agility to support diverse services. The incorporation of different cutting-edge technologies such as Network Function Virtualization (NFV), Software Defined Networking (SDN), Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) and Network Slicing has been envisioned as a solution for network transformation. Read this blog to explore the evolution of the mobile communication network to realize an innovative architecture.
The Architectural Evolution towards 5G SBA
Typically, a Mobile Communication Network (MCN)consists of two main parts: Radio Access Network (RAN) and the Core Network (CN). The RAN is composed of transceivers/base stations/access points that wirelessly connect to end-users. Whereas the CN is responsible for the macro mobility services. MCN is a shared network where multiple users are trying to access the network simultaneously. The network tries to understand the transactions between these users through the Control Plane (CP) and User Plane (UP). The CP transactions consist of call/session setup, maintenance, and call termination supporting required quality, while UP transactions cover the transfer of actual data/exchange of packets between users.
The development of 4G framework resulted in the evolution of smartphones and tablets. However, 4G may not be able to manage the enormous number of Internet of Things (IoT) connections that will be on the network in the coming years. It is expected that there will be billions of connected devices (tiny sensors), all of which will require a connection with great capacity. This is where 5G comes into force. 5G will be able to handle current devices and emerging technologies such as driverless cars, Industrial IoT (IIoT) applications, and more. Architectural changes are essential to support specific requirements of ultra-low latency and higher reliability in futuristic services.
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP)-based 5G network architecture is entirely different from the previous mobile network generations such as 2G/3G/4G LTE networks which is hierarchical. However, 5G network combines legacy technologies and is designed to cover smartphones as well as billions of tiny IoT sensors connected to the network. The RAN in 5G is a New Radio (NR) and the CN has a comprehensive remodel of the design.
How is 5G different from its predecessors?
In contrast to previous cellular generations, 5G network is based on: –
- Softwarization of Network & IT: Virtualized Network Functions (VNFs) utilizing Network NFV principles
- NFV runs VNFs on the top of general-purpose hardware replacing dedicated network appliances. With NFV, network operations such as routing, load balancing, and firewall becomes network function software delivered by Virtual Machines (VMs), which are dynamically instantiated in the network on demand
- Separation of Control & User planes
- Support for Centralized and Distributed processing etc.
- Network slice-based approach of utilizing the physical network resources
- MEC for delivering & processing low latency content and data
- MEC architecture enables computing capabilities close to users or at the network edge. Edge refers to the Data Centers (DCs) close to the RAN. The edge computing reduces core network traffic, signalling load and end–to-end latency thus improving service environment and user experience
- Providing cellular connections to things & devices and supporting extremely high density
- Handling advanced analytics
- Network capability exposure via Application Programming Interface (APIs) and Service Bus. API is set of protocols that allows two applications to talk to each other.
What is 5G SBA?
The network transformation is introduced to the 5G CN with a modular and cloud-native approach. The overall CN architecture is transformed to a Service-Based Architecture (SBA), facilitating agile and flexible services.
The 5G architecture, especially the CN has evolved from 4G architecture in two phases:
- Control and User Plane Separation (CUPS) of the 4G Core Network or Evolved Packet Core (EPC)
- Changing the 4G EPC CUPS functions into services
The 5G core network is remodeled on the control plane, user plane, and the transport plane. The control plane signaling within the CN is now basically based on the Service Based Architecture (SBA) design, introducing web-based technologies and the related security solutions.
Service-oriented architectures enhance the modularity of products in the software industry, where services are provided via a communication protocol over a network. This enables the breaking down of software products into communications services. Service-oriented architecture is not confined to specific vendors, products, and technologies. This technique allows developers to combine and match services from separate vendors into a specific product.
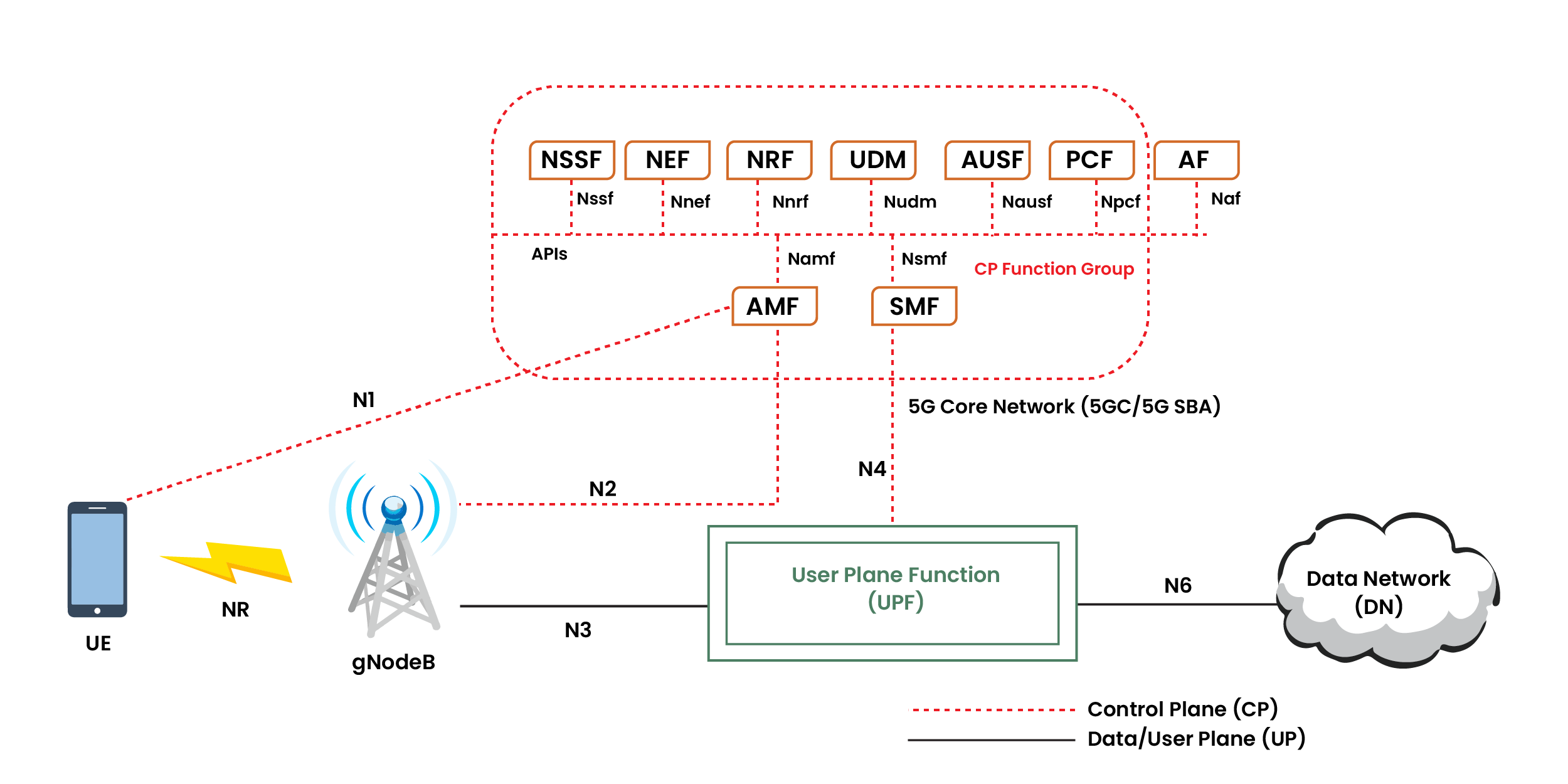
5G network will be unique with the SBA to deliver services for the new vertical industries such as Healthcare, Public Safety, Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and more. In 5G SBA, all the network elements are defined based on Network Functions (NFs), which communicate with each other over a Service-Based Interface (SBI). 5G SBA defined by 3GPP introduces a set of NFs to provide the control and user plane functionalities. SBA utilizes the concept of network slicing within the 5G Core (5GC) to provide insights into the application scenario. The 5GC network is based on SBA as shown in Figure 1, with web-based APIs, which enables a more flexible and agile deployment of innovative services. The table shows the functionalities of each network element in the 5G framework.
5G Network Elements Functionalities
| 5G Network Elements | Functionalities |
| Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF) | Access and mobility control, UE Registration. AMF also ends non-access stratum (NAS) signaling |
| Session Management Function (SMF) | Session management and control user plane traffic |
| User Plane Function (UPF) | UPF is responsible for packet forwarding and routing. It performs packet inspection and Quality of Service (QoS) implementation. |
| Network Slice Selection Function (NSSF) | Support network slice selection. Selects Network slice instances to serve the User Equipment (UE) |
| Network Repository Function (NRF) | Maintain NF profile and their functions. Helps to discover connections between NFs |
| Network Exposure Function (NEF) | Expose securely network capabilities and events |
| Unified Data Management (UDM) | Stores the subscriber information to support identification, access authorization and billing |
| Authentication Server Function (AUSF) | Stores authentication keys to authenticate UEs |
| Policy Control Function (PCF) | Maintain network policies to manage network behavior |
| Application Function (AF) | Fulfils the role of application server. Interacts with 5GC to provide services |
| gNodeB | Hardware that connects to the network and communicates wirelessly with UEs |
| Data Network (DN) | External network as Internet |
Benefits of 5G SBA
In SBA, the approach is to evolve and develop network capabilities centered on the new generation of services presented in the 5G era. The key advantages of SBA are as follows:
- In SBA, NFs capabilities are exposed via Representational State Transfer (REST) APIs and based out of HTTP2.0 protocol. Interconnection between NFs can be based on the Request/Response model or Subscribe/Notify model for availing the different 5G Services. This helps the Application-driven Digital Service Providers which require agility and quicker Time-To-Market (TTM) for the products/services rollouts
- The modularity of NFs and support of dynamic programmability enable the concept of network slicing in 5G. Multiple logical networks can be instantiated on-demand to serve different services simultaneously.
- Enables unified incorporation of third-party applications with the core network supporting mutli-vendor plug and play solutions
- Deploys NFs as containers with modular and cloud-native solutions. This helps in faster innovation and quick service delivery
The 5G Standalone (5G-SA) network will leverage the full potential of SBA, enhancing the customer experience while also introducing monetization and partnership opportunities for MNOs.
In Brief
5G SBA is a programmable framework design for the interconnection of 5G NFs in the Core and exposure of network capabilities & resources through SBI. This next generation 5G core network can realize innovative 5G services and solutions, leading to superior flexibility, scalability, and efficiency in the network.
Calsoft, being a Technology-First partner, can accelerate the network transformation journey, with our expertise in innovative technologies such as NFV, SDN, VNF development, and more. Choose Calsoft for trusted expertise and success in the dynamic world of Networking and Telecom.






