Commonly referred to as being “born in the cloud,” the cloud-native approach now encompasses the best of software development techniques such as DevOps, Containerization, Microservices, Agile methodology, and more. According to the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF), “cloud-native technologies empower organizations to build and run scalable applications on dynamic cloud environments.”
Since the pioneering success of cloud-native architecture by streaming giant, Netflix, many technology companies and application developers have adopted the cloud-native development approach to build efficient cloud applications. Promising a rapid release cycle and workload management, cloud-native apps are powering digital transformation by allowing the change from being a “business support” to being the “business itself.”
As cloud platforms move into this new “avatar,” how should cloud app developers adapt to the new paradigm and avoid common pitfalls? Our blog is curated to help understand the fundamentals of cloud-native app development and focuses on sharing valuable insights on the top 5 best practices in the realm of cloud-native application development. Stay with us to garner comprehensive information on how to navigate this dynamic landscape and ensure that your cloud-native applications are robust, scalable, and efficient.
What is the Cloud Native Approach
Cloud-native application development is the art of developing and managing modern applications in cloud environments. It is an approach that supports the idea of developing an app from inception to reality by taking complete advantage of the cloud computing model. As competition is on the rise, modern businesses are keen on building highly scalable, agile, and resilient applications that can be upgraded at any time based on customer demand. Cloud-native technologies do the same, without hampering service delivery, or quality and by offering a competitive advantage.
Benefits of the Cloud-Native Approach
By leveraging cloud-native technologies, businesses can ensure:
- Faster Time-to-Market:
Developers use the cloud-native approach to dramatically save time by not relying on any hardware infrastructure. By deploying the cloud model, they eliminate traditional development obstacles and are in a position to develop, test, and add features at a rapid pace.
- Cost Efficiency:
The bottom line of moving to the cloud is cost reduction. Similarly, opting for cloud-native development helps businesses save money eliminating the need of repetitive investments in hardware to build, test, or run applications. The entire responsibility is taken by the cloud provider.
- Enhanced Reliability:
Cloud-native applications include redundancy and fault tolerance, leading to reduction in downtime and maintaining steady performance. This ensures that services remain reliable and consistently available, even during unexpected issues.
- Improved Security:
Similar to DevSecOps, the cloud-native approach integrates security into every stage of the SLDC, ensuring robust protection against threats.
- Greater Innovation:
Away from the limitations of traditional infrastructure, in the cloud-native setup, developers get an opportunity to experiment with new technologies, platforms, and methodologies to drive continuous improvement and innovation.
We agree that going cloud-native might not be as easy as it sounds. However, to streamline this journey, we have carefully curated a blog that speaks about 6 intricate challenges in going cloud-native and also share the perfect solution.
Cloud-Native Development – Key Principles
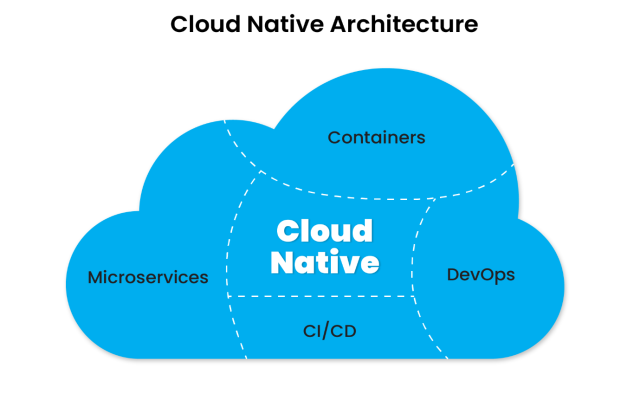
The cloud-native development process is usually based on the following 4 key principles:
- Microservices or the development architecture where larger applications are built using a suite of individual components or modular services.
- Containerization or the use of software containers to package and isolate applications to be run independently from the physical resources.
- Continuous delivery and integration, also known as (CD/CI), can be deployed by software testing teams to test shorter code bases in continuous release cycles.
- DevOps methodology automates the application lifecycle and enables better collaboration between the development and operations teams.
Furthermore, it is essential to understand how cloud-native apps differ from cloud-based apps. Cloud-based apps are designed to work on the cloud but do not fully leverage the capabilities of the cloud. On the other hand, cloud-native apps are designed specifically for dynamic cloud environments and are optimized for cloud characteristics such as resource pooling, rapid scalability & elasticity, and on-demand service. The difference is especially stark over the application development process as a result.
5 Core Elements of Cloud-native Applications
Next, let’s look at the 5 core elements of cloud-native applications that must be integrated to achieve optimal performance and scalability.
Here are the 5 core elements of any cloud-native app:
- Application Design
Cloud-native apps are designed for speed in both delivery and iterations. Hence, the application’s design needs to be based on the microservices architecture, which is crucial for making the app adaptable and flexible for the cloud.
How do microservices address the concerns posed by monolithic architecture?
- Each microservice module is updated and executed independently without affecting other modules.
- It can accelerate the deployment of new functionality without the need to integrate the updated code with other microservice code.
- Eliminates the need to deploy the complete executable code (as in monolithic apps) that is time-consuming and inflexible for erratic workloads.
How do microservices-based apps communicate with different services? Using RESTful APIs makes it easier to accept and respond to service requests. Effectively, APIs act as the “glue” among the loosely coupled microservices. APIs make it easier for external service callers to format a service request and communicate with the cloud-native apps, irrespective of their location on the same network or across the internet.
A proper call format with adequate identification and authentication contains an accurate payload, thus enabling the correct execution of the service.
- DevOps
On its part, DevOps is designed to reduce the lengthy durations between application deployments caused by “IT silos.” For the fast deployment and implementation of cloud-native apps, DevOps needs to be a core element that effectively breaks down the barriers between the development and production stages.
To initiate the DevOps process, organizations can useValue Chain Mapping (VCM) that can evaluate the complete application development cycle. The VCM technique can optimize each “silo” and automate a group’s work while not disturbing other groups.
- Operational Design
A single executable of the monolithic architecture required the entire application code to be deployed to the production environment. Cloud-native apps simplify the operational design through microservices, where code modifications are limited to individual executables, leaving the rest of the app code unchanged.
As a core element, the microservices-based operational design ensures:
- Better operational efficiency during any changeover
- Simpler and easier rolling out of code changes
- Easier recreation of the older production environment when code issues are reported
- Quality Assurance (QA)
- Quality Assurance (QA)
The importance of QA and testing cannot be underestimated in the cloud-native app development process. The approach ensures that QA is performed at an earlier stage in the app development, to detect and address issues. Further, this approach ensures that app developers now own the responsibility to test “new functionalities” that they develop.
This approach allows QA teams to focus on other testing aspects including integration testing, performance testing, and testing on multiple devices.
To better understand how cloud-native applications are better, refer to the table below that shares comparison points between Monolithic Architecture and Microservices Architecture.
| Aspect | Monolithic Architecture | Microservices Architecture |
| Structure | Single, unified codebase | Composed of multiple independent services |
| Deployment | Deployed as a single unit | Each service can be deployed independently |
| Scalability | Vertical scaling (adding more resources to a single node) | Horizontal scaling (adding more instances of individual services) |
| Development | Requires coordination for any changes | Teams can work on different services simultaneously without much coordination |
| Technology Stack | Typically uses a single technology stack | Allows the use of different technologies for different services |
| Fault Isolation | A failure in one component can affect the entire application | Faults are isolated to individual services, reducing the impact on the entire application |
| Testing | Integration testing can be complex and time-consuming | Easier to test individual services, but requires coordination for end-to-end testing |
| Performance | Potential performance bottlenecks due to tightly coupled components | Improved performance as services can be optimized and scaled independently |
| Maintenance | Can become difficult to maintain and update over time | Easier to update and maintain individual services without affecting the entire system |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, as changes affect the entire system | More flexible, as individual services can be modified or replaced without impacting other services |
| Deployment Speed | Slower, as the entire application needs to be redeployed | Faster, as only the changed services need to be redeployed |
5 Best Practices in Cloud-native Development
Cloud-native applications are often built from the ground up to be able to run on public cloud platforms. Well, there ideally are no set rules for developing these apps. In fact, the entire development strategy is focused on the business problem the software is going to be used to resolve. However, to be able to deploy the goodness of cloud-native development to the advantage of your business, it is most recommended to have a fair idea about the industry best practices that can make the journey better and derive superior results from your development efforts.
So, without any further ado, let’s find out what these top 5 best practices related to cloud-native development have in store.
1. Go Serverless
Harnessing the power of serverless technologies is a great choice to enhance the scalability and efficiency of cloud-native applications. Serverless computing enables developers to run code, integrate, and manage data without having to provision or manage servers. This means the entire focus can be on writing and deploying the code. Additionally, going serverless enables automatic scaling. This means your application is automatically adjusted based on the current demand, ensuring maximum performance and cost-efficiency.
2. Embrace Microservices
Increase application flexibility by using a microservices architecture, which efficiently allocates resources to individual services. Each service focuses on a specific business goal, maintains its own data, and communicates with other services through APIs, ensuring modularity and independent scalability.
3. Go for Appropriate Languages and Frameworks
Cloud-native applications are designed specifically for the cloud, leveraging its capabilities to enhance speed, flexibility, and quality while minimizing deployment risks. These applications can utilize various languages, runtimes, and frameworks. Therefore, it’s crucial to select the language and framework that best suits the specific functionality and requirements of your application.
4. Automate the Release Pipeline
Implement continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) to expedite the release of high-quality code. CI involves developers merging code changes into a central repository, followed by automated builds and tests. CD automates the preparation of code changes for production deployment, ensuring faster and more frequent releases.
5. Take a Modern, Multi-faceted Approach to Security
Align security with the dynamic nature of cloud-native applications by adopting DevSecOps practices. Employ a defense-in-depth strategy and integrate security into development workflows. Automate and orchestrate threat mitigation processes and ensure continuous security testing is intrinsic to the development lifecycle.
Besides these best practices, there are plenty of development tools that can be used for cloud-native apps. These tools, formed in most cloud-native development stacks, include the Docker platform (for managing virtualized app containers), Kubernetes (for managing Linux containers), and Terraform (for managing IaC services).
Conclusion
The best use of cloud-native application development can empower businesses to develop and run scalable applications on various cloud environments such as private, public, and hybrid. Additionally, the use of containers, mesh, microservices, and more exemplify this approach to deliver high-quality and high-impact products. So, if you are building software using the cloud-native approach, it is essential to take full advantage of the cloud computing model. According to an annual survey by the CNCF recently, 30% of respondents have adopted cloud-native approaches almost in all development activities. Similarly, a report by Tigera states that 75% of all companies are now focused on cloud-native application development. These numbers clearly state the rate at which this technology is being accepted and adopted.
Remember, cloud-native app development eliminates a range of limitations associated with traditional monolithic architecture. Therefore, if you want to change the software development game and stay ahead of the competition, it is recommended to embrace cloud native practices.
At Calsoft we take the cloud seriously. With 25+ years of experience in software product engineering services and extensive domain experience, we have transformed business operations for many companies through innovative cloud solutions, ensuring your business growth is multiplied and products are cloud ready.






