This article is originally published on TheNewStack. We are re-publishing it here.
Leading tech giants and multiple enterprises are investing heavily in edge computing solutions. The edge computing will enable businesses to act faster after consuming data and stay on top of the competition. Faster actions expected by innovative applications will need near real-time access to data, process data to nearby edge node and generate insights to feed the cloud and originating devices. Edge solution vendors are building edge solutions to reduce the impact of latency on different business use cases.
The goal of edge computing enabled network should be to maintain the end-to-end quality of service and user experience continuity in a network where edge nodes are active. As an example, considering edge will be mainstream in 5G-telecom network, a 5G subscriber should not lose the active services while moving within different edge premises. Also, new services need to push in real time irrespective of any edge zone in the network. A subscriber will demand not just new services on a consistent basis but in a faster way to realize 100 percent outcome for real-time applications. As IoT is evolving in technology market landscape, such low latency demand will be higher from consumers to network operators and solution providers.
On the same lines, the Red Hat team proposed the integrated solution to reduce latency and maintain user experience continuity within a 5G network enabled with edge nodes. Let us get an overview of the same.
[eBook] 5G Architecture: Convergence of NFV & SDN Networking Technologies.
Download ebook to know about technologies behind 5G network and status of adoption of 5G along with key insights into a market in this ebook.
Co-Location of Ceph and OpenStack Together in a Hyper-Converged Fashion
5G network is been characterized with distributed cloud infrastructure in which services are set to deliver at every part of network i.e. from central data center/cloud to regional and edge. But, having distributed edge nodes connected to a central cloud comes with constraints in case of 5G network.
- The basic requirement for service providers is to lifecycle management of network services to every node in the network, have a centralized control on those functions and end-to-end orchestration from a central location.
- A 5G network should provide lower latency, higher bandwidth along with resiliency (failure and recovery at a single node) and scalability (of services as per increasing demands) at edge level.
- Service providers will need to provide faster and reliable services to consumers with minimum hardware resources, those mainly at regional nodes and edge nodes.
- A huge amount of data processing and analysis to be taken place at edge nodes. This will require storage systems that can store every type of data in all available ways and faster access to that data.
To address the above needs, Red Hat’s Sean Cohen, Giulio Fidente and Sébastien Han proposed the solution architecture in OpenStack Summit Berlin, November 2018. The architecture amalgamates OpenStack’s core as well as storage-related projects with Ceph in a hyperconverged way. The resultant architecture will support distributed NFV (which is backbone technology for 5G), emerging use cases with fewer control planes and distribute VNFs (Virtual Network Functions or network services) within all regional and edge nodes involved in network.
Proposed solution referred Akraino Edge Stack (Software stack for Edge, Linux Foundation Open Source Project), a typical edge architecture consists of Central site/data center/cloud, regional site and far edge site.
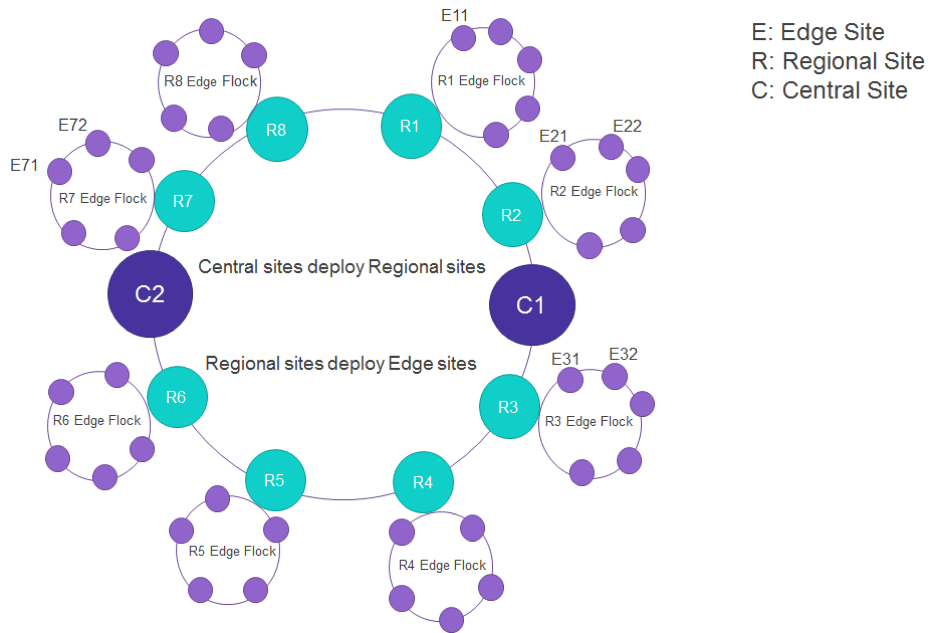
A central cloud is the backbone of all operations and management of a network where all processed data can be stored. Regional sites or edge nodes can be mobile towers, a node dedicated to specific premises or any other telco-centric premises. Far edge nodes are endpoints of a network which can be digital equipment like mobiles, drones, smart devices; autonomous vehicles, industrial IoT equipment, etc. Shared storage is available at edge zone to make persistent to survive in case of node failure.
Deployment Proposed in Solution
In this proposed solution, Edge Point of Delivery (POD) architecture for Telco service providers are referred by the Red Hat team to explain where Ceph clusters can be placed with OpenStack project in a hyperconverged way.
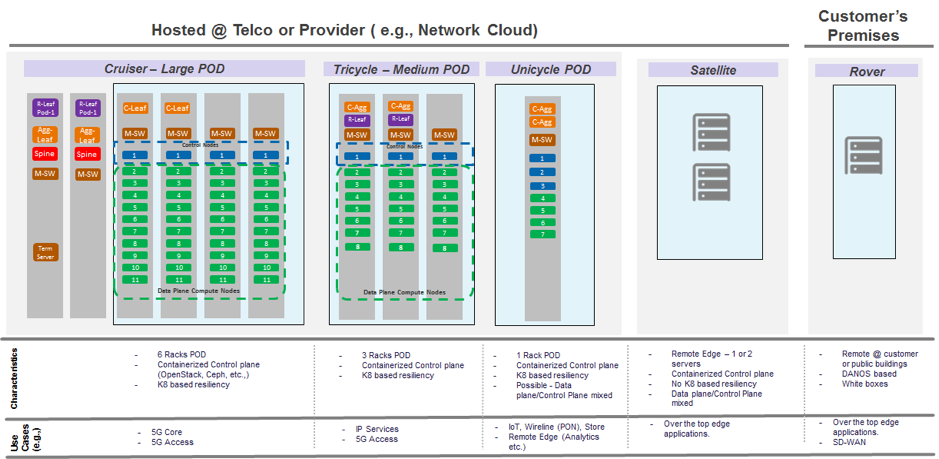
Based on the above diagram, let’s understand the deployment and operations scenarios.
OpenStack
In the case of figure 2, OpenStack already covers the support for Cruiser and Tricycle of POD. But, for edge deployments, different projects of OpenStack can be utilized for various operations.
TripleO: A proposed TripleO architecture targeted to reduce the control planes from central cloud to far edge nodes using OpenStack TripleO controller node at the middle layer. The proposed solution is to make TripleO capable of deploying non-controller nodes that are at the edge. With the power of TripleO, OpenStack can have central control over all the edge nodes participated in the network.
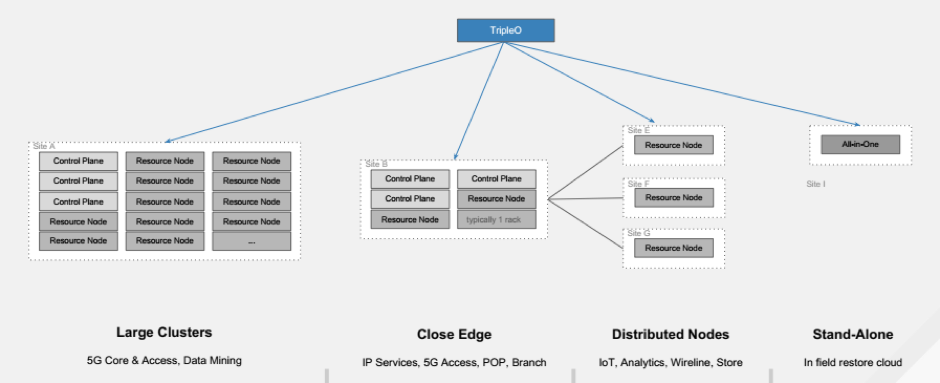
Glance API: It will mainly responsible for workload delivery in form of VM images in the edge network from the central data center to far edge nodes. Glance is set up at to central data center and deployed it on the middle edge node where the controller resides. Glance API with a cache can be pushed at far edge site, which is hyperconverged. This way images can be pulled to far edge nodes from the central data center.
Ceph
Ceph provides different interfaces to access your data based on the object, block, or file storage. In this architecture, Ceph can be deployed in containers as well as a hypervisor as well. Containerizing Ceph clusters brings more benefits to dynamic workloads. Like better isolation, faster access to applications, better control on resource utilization, etc.
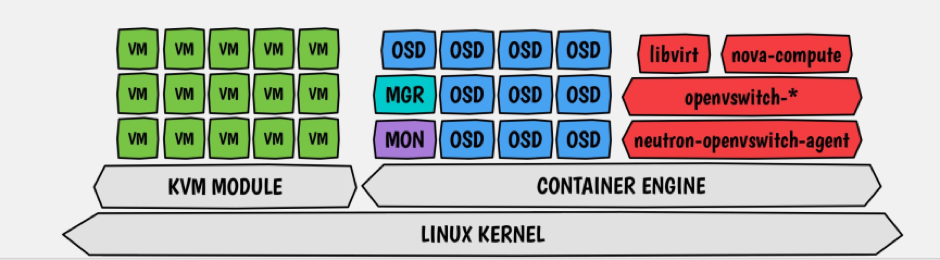
Deployment of Ceph in hyperconverged should be done at Unicycle and Satellite PODs (refer to figure 2) that is the edge nodes; right after central cloud. Therefore, a resultant architecture, which depicts the co-location of containerized Ceph clusters at a regional site, looks like below. Such co-location can (refer to figure 2).
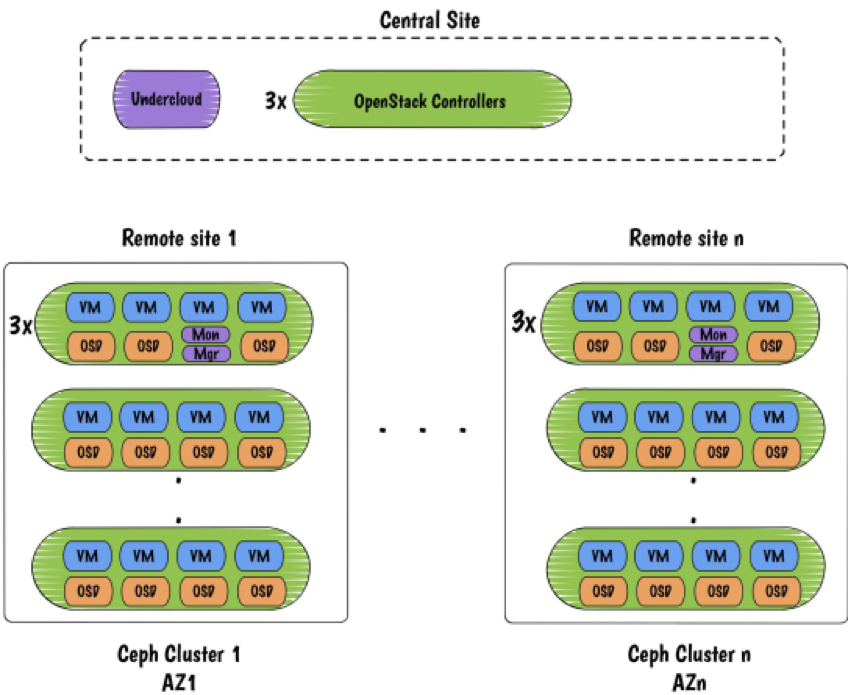
Ceph deployed with two packages Monitor and Manager; to bring monitoring benefits such as gathering info, managing maps and storing them.
The representation shows the control plane is detached from decedent nodes and put on a central site. This brings benefits such as
- Reduction of hardware resources and cost at the edge as edge nodes are hyperconverged and no control plane required to manage each node.
- Better utilization of compute and storage resources.
- Reduction of deployment complexity
- Reduction in operational maintenance as control plane will be similar across all edge nodes and unified lifecycle will be followed for scaling, upgrades, etc.
Final Architecture (OpenStack + Ceph Clusters)
Here is the overall architecture from the central site to far edge nodes comprising the distribution of OpenStack services with integration in Ceph clusters. The representation shows how projects are distributed; control plane projects stack at central nodes and data stacks for far edge nodes.
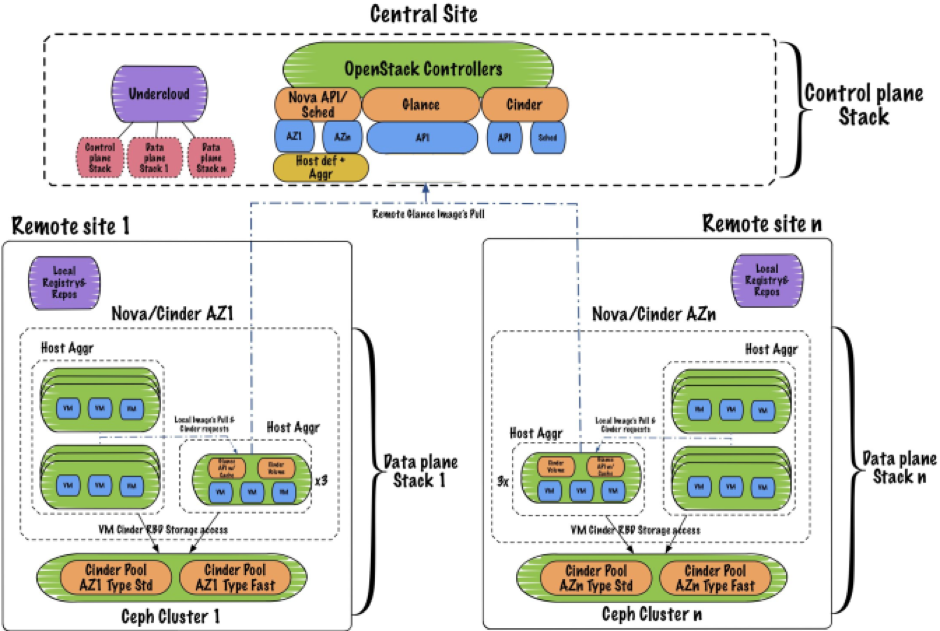
There are few considerations and future work involved in upcoming OpenStack release “Stein.” It will involve focussing on service sustenance when edge nodes disconnections, no storage requirement at the far edge, HCI with Ceph Monitors using containers resource allocations, ability to deploy multiple Ceph clusters with TripleO, etc.
Summary
Hyperconvergence of hardware resources is expected to be a fundamental architecture for multiple mini data center i.e. edge nodes. Red Hat team came with an innovative hyperconvergence of OpenStack projects along with Ceph software-defined storage. A solution shows, it is possible to gain better control all edge nodes by reducing control planes and maintain the continuity and sustainability of 5G network along with the performance required by new age applications.






