We are republishing this blog here. Earlier, it was published on RTinsights.
IoT is growing fast, and so too the need for edge computing that enables the processing of information closer to IoT devices. Kubernetes is the proven and disruptive open source technology for operators and developers that addresses operational and technical concerns of managing tons of applications deployed at the edge. Today, we have several Kubernetes distributions like K3S, KubeEdge, or MicroK8S that you can use to get started quickly to deal with edge requirements.
Edge nodes are devices that are of different scale. There are heavy edge servers that sit at one department in case of industrial IoT or in the stores in a retail chain. A light edge server is a small server that is connected to end IoT devices. Heavy and light servers can be a part of a Kubernetes cluster because of the hardware capacities they have. But it is hard for end IoT devices to become part of Kubernetes clusters, which are dedicated to a single function and host small embedded applications to gather data. For example, take sensors or video cameras. It is important that these devices be a part of Kubernetes architecture so that outputs can be obtained via edge or cloud seamlessly.
With the growing number of such edge devices, it becomes harder to manage subsequent edge servers that host Kubernetes clusters. The addition and removal of new devices cause more work to operators. They must find and allocate resources and monitor availability within the architecture. Also, at some point in time, you will need to add more servers to handle more edge devices. Such issues call for better intelligence for edge devices that will handle the presence of edge IoT devices in Kubernetes clusters. Akri does that. It is an open-source project released by Microsoft.
The Akri framework helps expose IoT devices as resources and creates services for each device in Kubernetes clusters. That makes it possible for applications to consume the inputs from the devices. Akri handles the automatic inclusion and removal of IoT devices, as well as the allocation and deallocation of resources to better optimize the clusters. With the power of Akri, it is possible to add as many IoT devices dynamically and inferencing nodes to process data from those devices. Moreover, you can seamlessly introduce a new server environment when there are more requirements to add edge IoT devices.
Akri supports the handling of network-connected IoT edge devices like IP cameras, controllers, PoS (point of sale) terminals, and devices connected locally through Kubernetes nodes such as USB-connected sensors. It schedules the workloads based on the availability of devices at the Kubernetes cluster. It uses the abstraction layer that is like a Container Network Interface (CNI). But instead of abstracting the underlying network details, it removes the work of finding, utilizing, and monitoring the availability of devices. Thus, drastically reduce the amount of work done by Kubernetes admins and developers.
Akri is based on the Kubernetes device plugin framework, which is used by vendors for static resources allowing them to advertise their resources and monitor them without writing additional codes. Akri extends this framework to edge in an environment that has different sets of devices and various protocols to monitor and communicate with those edge IoT devices.
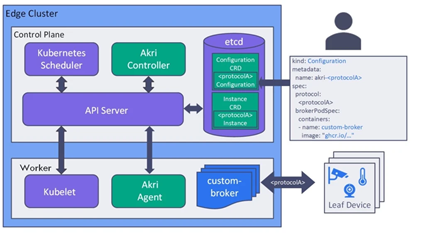
In a typical Kubernetes edge cluster, it adds four components: Akri Controller, Akri Agent (Kubernetes device plugin framework implementation), and two CDRs (Custom Resource Definition) (for configuration and instance). These components work together to find edge IoT devices and schedule workloads among those. The Akri agent can be deployed to each new worker edge node.
In a nutshell,
- Akri handles the appearance and disappearance of edge IoT devices and schedule workloads in a cluster
- Akri provides the interface where you provide the configuration using configuration CRDs, and Akri does the rest.
- Operators are assured of high availability of edge nodes in case other nodes go down.
- As Akri creates Kubernetes services for each edge IoT device, applications do not need trace state of pods or edge nodes.
You can contribute to the Akri project on Github and join the discussion on their Slack channel.
Conclusion
Using Kubernetes for edge is an exciting development that enormously enables consistency in application policies, end-to-end automation, and faster services deployment and scaling. Akri brings a more simplified approach that allows more control on all parts of the edge-enabled network and makes life easier for Kubernetes admins and developers.






